Update on Merkel Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 29556962
- PMCID: PMC5873498
- DOI: 10.1007/s12105-018-0898-2
Update on Merkel Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) is an aggressive cutaneous neuroendocrine carcinoma. Incidence of MCC continues to rise, and risk factors include advanced age, pale skin, chronic sun exposure, and immune suppression. Diagnosing MCC utilizes a combination of morphology and immunohistochemistry. Merkel cell polyomavirus (MCPyV) is present in approximately 70-80% of MCCs and represents a key pathogenic driver in those MCCs. In contrast, MCPyV-negative MCCs arise through progressive accumulation of ultraviolet-light induced somatic mutations. Staging of MCC proceeds according to the American Joint Commission on Cancer (AJCC) 8th Edition, which utilizes features of the primary tumor together with regional lymph node(s) (clinically and/or pathologically detected) and/or distant metastases. Many potentially useful biomarkers have been studied to refine risk stratification in MCC. In recent years, the host immune infiltrate has been leveraged as immune checkpoint blockade has emerged as an efficacious mode of treatment for patients with advanced MCC.
Keywords: Merkel cell carcinoma; Merkel cell polyoma virus; Pathogenesis; Prognostic factors; Staging.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
MTT has received an honorarium from Myriad Genetics, Seattle Genetics and Novartis for Advisory Boards. MTT declares no relevant conflicts of interest to the material presented herein.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors. This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Figures

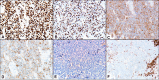
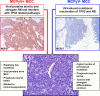
References
-
- Fitzgerald TL, Dennis S, Kachare SD, Vohra NA, Wong JH, Zervos EE. Dramatic increase in the incidence and mortality from Merkel cell carcinoma in the United States. Am Surg. 2015;81(8):802–806. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

