Substantial Decrease in Plasmalogen in the Heart Associated with Tafazzin Deficiency
- PMID: 29557170
- PMCID: PMC5893435
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.biochem.8b00042
Substantial Decrease in Plasmalogen in the Heart Associated with Tafazzin Deficiency
Abstract
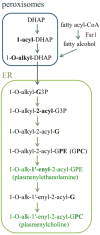
Tafazzin is the mitochondrial enzyme that catalyzes transacylation between a phospholipid and a lysophospholipid in remodeling. Mutations in tafazzin cause Barth syndrome, a potentially life-threatening disease with the major symptom being cardiomyopathy. In the tafazzin-deficient heart, cardiolipin (CL) acyl chains become abnormally heterogeneous unlike those in the normal heart with a single dominant linoleoyl species, tetralinoleoyl CL. In addition, the amount of CL decreases and monolysocardiolipin (MLCL) accumulates. Here we determine using high-resolution 31P nuclear magnetic resonance with cryoprobe technology the fundamental phospholipid composition, including the major but oxidation-labile plasmalogens, in the tafazzin-knockdown (TAZ-KD) mouse heart as a model of Barth syndrome. In addition to confirming a lower level of CL (6.4 ± 0.1 → 2.0 ± 0.4 mol % of the total phospholipid) and accumulation of MLCL (not detected → 3.3 ± 0.5 mol %) in the TAZ-KD, we found a substantial reduction in the level of plasmenylcholine (30.8 ± 2.8 → 18.1 ± 3.1 mol %), the most abundant phospholipid in the control wild type. A quantitative Western blot revealed that while the level of peroxisomes, where early steps of plasmalogen synthesis take place, was normal in the TAZ-KD model, expression of Far1 as a rate-determining enzyme in plasmalogen synthesis was dramatically upregulated by 8.3 (±1.6)-fold to accelerate the synthesis in response to the reduced level of plasmalogen. We confirmed lyso-plasmenylcholine or plasmenylcholine is a substrate of purified tafazzin for transacylation with CL or MLCL, respectively. Our results suggest that plasmenylcholine, abundant in linoleoyl species, is important in remodeling CL in the heart. Tafazzin deficiency thus has a major impact on the cardiac plasmenylcholine level and thereby its functions.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Tafazzin deficiency impairs CoA-dependent oxidative metabolism in cardiac mitochondria.J Biol Chem. 2020 Aug 28;295(35):12485-12497. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.011229. Epub 2020 Jul 14. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32665401 Free PMC article.
-
SS-31 treatment ameliorates cardiac mitochondrial morphology and defective mitophagy in a murine model of Barth syndrome.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 13;14(1):13655. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-64368-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38871974 Free PMC article.
-
Plasmalogen loss caused by remodeling deficiency in mitochondria.Life Sci Alliance. 2019 Aug 21;2(4):e201900348. doi: 10.26508/lsa.201900348. Print 2019 Aug. Life Sci Alliance. 2019. PMID: 31434794 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between cardiolipin and plasmalogens in Barth syndrome.J Inherit Metab Dis. 2022 Jan;45(1):99-110. doi: 10.1002/jimd.12449. Epub 2021 Oct 21. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2022. PMID: 34655242 Review.
-
Cardiolipin remodeling: a regulatory hub for modulating cardiolipin metabolism and function.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2016 Apr;48(2):113-23. doi: 10.1007/s10863-014-9591-7. Epub 2014 Nov 29. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2016. PMID: 25432572 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tricky Isomers-The Evolution of Analytical Strategies to Characterize Plasmalogens and Plasmanyl Ether Lipids.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Apr 27;10:864716. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.864716. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35573699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Marine Plasmalogens: A Gift from the Sea with Benefits for Age-Associated Diseases.Molecules. 2023 Aug 29;28(17):6328. doi: 10.3390/molecules28176328. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37687157 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PEX3 promotes regenerative repair after myocardial injury in mice through facilitating plasma membrane localization of ITGB3.Commun Biol. 2024 Jul 1;7(1):795. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-06483-0. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 38951640 Free PMC article.
-
Rosy Beginnings: Studying Peroxisomes in Drosophila.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Aug 25;8:835. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00835. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32984330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Barth Syndrome Cardiomyopathy: An Update.Genes (Basel). 2022 Apr 8;13(4):656. doi: 10.3390/genes13040656. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35456462 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kimura T, Jennings W, Epand RM. Roles of specific lipid species in the cell and their molecular mechanism. Prog Lipid Res. 2016;62:75–92. - PubMed
-
- Barth PG, Scholte HR, Berden JA, van der Klei-van Moorsel JM, Luyt-Houwen IEM, van’t Veer-Korthof ET, van der Harten JJ, Sobotka-Plojhar MA. An X-linked mitochondrial disease affecting cardiac muscle, skeletal muscle and neutrophil leucocytes. J Neurol Sci. 1983;62:327–355. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

