Effects of the Phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE-5) Inhibitors, Avanafil and Zaprinast, on Bone Remodeling and Oxidative Damage in a Rat Model of Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis
- PMID: 29557941
- PMCID: PMC5865409
- DOI: 10.12659/MSMBR.908504
Effects of the Phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE-5) Inhibitors, Avanafil and Zaprinast, on Bone Remodeling and Oxidative Damage in a Rat Model of Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of the phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE-5) inhibitors, zaprinast and avanafil, on NO signalling pathway, bone mineral density (BMD), epiphyseal bone width, bone marrow angiogenesis, and parameters of oxidative stress in a rat model of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis (GIOP).
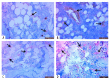
Material/Methods: Twenty-four 8-month-old male rats in four groups were given a single daily treatment during a 30-day period: an (untreated) control group (n=6): a dexamethasone-treated group (120 μ/kg) (n=6); a group treated with dexamethasone (120 μ/kg) and zaprinast (10 mg/kg) (n=6): and a group treated with dexamethasone (120 μ/kg) and avanafil (10 mg/kg) (n=6). Rat whole body bone mineral density (BMD) was measured by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA), and bone histology was performed. Also, selected oxidative stress parameters by HPLC method and the other biochemical parameters by ELISA method were measured.
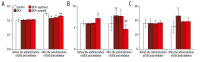
Results: The GIOP model rats treated with zaprinast and avanafil showed a significant increase in NO, cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), and protein kinase G (PKG) (NO/cGMP/PKG) signaling-pathway components, and in C-terminal telopeptide of type I collagen (CTX-1), bone marrow angiogenesis, BMD, and epiphyseal bone width, compared with the (untreated) control rats (p<0.05). Levels of pyridinoline (PD) and deoxypyridinoline (DPD) were significantly reduced in the dexamethasone + zaprinast, and dexamethasone + avanafil treatment groups (p<0.05). Malondialdehyde (MDA), ubiquinone-10 (CoQ10), ubiquinol CoQ10 (CoQ10H), and 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) were significantly increased in the dexamethasone-treated group, compared with the (untreated) controls (p<0.05).
Conclusions: In the GIOP rat model, markers of oxidative stress and bone atrophy were significantly reduced by treatment with the PDE-5 inhibitors, zaprinast and avanafil.
Keywords: Bone Density; Dexamethasone; Osteoporosis; Phosphodiesterase 5 Inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


References
-
- Shen G, Ren H, Qiu T, et al. Effect of glucocorticoid withdrawal on glucocorticoid inducing bone impairment. Biochem Biophy Res Commun. 2016;477:1059–64. - PubMed
-
- Zhang ZF, Min JK, Wang D, et al. Pinoresinol diglucoside exhibits protective effect on dexamethasone-induced osteoporosis in rats. Trop J Pharm Res. 2016;15:2451–57.
-
- Halici Z, Borekci B, Ozdemir Y, et al. Protective effects of amlodipine and lacidipine on ovariectomy-induced bone loss in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008;579:241–45. - PubMed
-
- Polat B, Halici Z, Cadirci E, et al. The effect of alpha-lipoic acid in ovariectomy and inflammation-mediated osteoporosis on the skeletal status of rat bone. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013;718:469–74. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

