Inhibition of hypoxia-associated response and kynurenine production in response to hyperbaric oxygen as mechanisms involved in protection against experimental cerebral malaria
- PMID: 29558201
- PMCID: PMC6044055
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.201700844R
Inhibition of hypoxia-associated response and kynurenine production in response to hyperbaric oxygen as mechanisms involved in protection against experimental cerebral malaria
Abstract
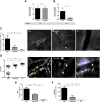
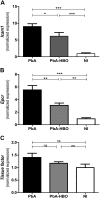
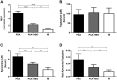
Cerebral malaria (CM) is a multifactorial syndrome involving an exacerbated proinflammatory status, endothelial cell activation, coagulopathy, hypoxia, and accumulation of leukocytes and parasites in the brain microvasculature. Despite significant improvements in malaria control, 15% of mortality is still observed in CM cases, and 25% of survivors develop neurologic sequelae for life-even after appropriate antimalarial therapy. A treatment that ameliorates CM clinical signs, resulting in complete healing, is urgently needed. Previously, we showed a hyperbaric oxygen (HBO)-protective effect against experimental CM. Here, we provide molecular evidence that HBO targets brain endothelial cells by decreasing their activation and inhibits parasite and leukocyte accumulation, thus improving cerebral microcirculatory blood flow. HBO treatment increased the expression of aryl hydrocarbon receptor over hypoxia-inducible factor 1-α (HIF-1α), an oxygen-sensitive cytosolic receptor, along with decreased indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 expression and kynurenine levels. Moreover, ablation of HIF-1α expression in endothelial cells in mice conferred protection against CM and improved survival. We propose that HBO should be pursued as an adjunctive therapy in CM patients to prolong survival and diminish deleterious proinflammatory reaction. Furthermore, our data support the use of HBO in therapeutic strategies to improve outcomes of non-CM disorders affecting the brain.-Bastos, M. F., Kayano, A. C. A. V., Silva-Filho, J. L., Dos-Santos, J. C. K., Judice, C., Blanco, Y. C., Shryock, N., Sercundes, M. K., Ortolan, L. S., Francelin, C., Leite, J. A., Oliveira, R., Elias, R. M., Câmara, N. O. S., Lopes, S. C. P., Albrecht, L., Farias, A. S., Vicente, C. P., Werneck, C. C., Giorgio, S., Verinaud, L., Epiphanio, S., Marinho, C. R. F., Lalwani, P., Amino, R., Aliberti, J., Costa, F. T. M. Inhibition of hypoxia-associated response and kynurenine production in response to hyperbaric oxygen as mechanisms involved in protection against experimental cerebral malaria.
Keywords: aryl-hydrocarbon receptor; brain; endothelial cell activation; tryptophan metabolism.
Conflict of interest statement
This work was supported by Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP) Grants 2012/16525-2 (to F.T.M.C.), 2014/20451-0 (to S.E.), 2016/07030-0 (to C.R.F.M.), and 2016/12855-9 (to J.L.S-F.); FAPESP (
Figures



References
-
- World Health Organization (2015) World Malaria Report 2015, World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland
-
- Idro R., Jenkins N. E., Newton C. R. (2005) Pathogenesis, clinical features, and neurological outcome of cerebral malaria. Lancet Neurol. 4, 827–840 - PubMed
-
- Dondorp A. M., Fanello C. I., Hendriksen I. C., Gomes E., Seni A., Chhaganlal K. D., Bojang K., Olaosebikan R., Anunobi N., Maitland K., Kivaya E., Agbenyega T., Nguah S. B., Evans J., Gesase S., Kahabuka C., Mtove G., Nadjm B., Deen J., Mwanga-Amumpaire J., Nansumba M., Karema C., Umulisa N., Uwimana A., Mokuolu O. A., Adedoyin O. T., Johnson W. B., Tshefu A. K., Onyamboko M. A., Sakulthaew T., Ngum W. P., Silamut K., Stepniewska K., Woodrow C. J., Bethell D., Wills B., Oneko M., Peto T. E., von Seidlein L., Day N. P., White N. J.; AQUAMAT group (2010) Artesunate versus quinine in the treatment of severe falciparum malaria in African children (AQUAMAT): an open-label, randomised trial. Lancet 376, 1647–1657; erratum, (2011) 377, 126 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

