UHRF1 epigenetically orchestrates smooth muscle cell plasticity in arterial disease
- PMID: 29558369
- PMCID: PMC5983314
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI96121
UHRF1 epigenetically orchestrates smooth muscle cell plasticity in arterial disease
Abstract
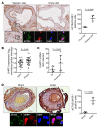
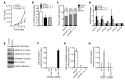
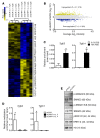
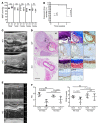
Adult vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) dedifferentiate in response to extracellular cues such as vascular damage and inflammation. Dedifferentiated VSMCs are proliferative, migratory, less contractile, and can contribute to vascular repair as well as to cardiovascular pathologies such as intimal hyperplasia/restenosis in coronary artery and arterial aneurysm. We here demonstrate the role of ubiquitin-like containing PHD and RING finger domains 1 (UHRF1) as an epigenetic master regulator of VSMC plasticity. UHRF1 expression correlated with the development of vascular pathologies associated with modulation of noncoding RNAs, such as microRNAs. miR-145 - pivotal in regulating VSMC plasticity, which is reduced in vascular diseases - was found to control Uhrf1 mRNA translation. In turn, UHRF1 triggered VSMC proliferation, directly repressing promoters of cell-cycle inhibitor genes (including p21 and p27) and key prodifferentiation genes via the methylation of DNA and histones. Local vascular viral delivery of Uhrf1 shRNAs or Uhrf1 VSMC-specific deletion prevented intimal hyperplasia in mouse carotid artery and decreased vessel damage in a mouse model of aortic aneurysm. Our study demonstrates the fundamental role of Uhrf1 in regulating VSMC phenotype by promoting proliferation and dedifferentiation. UHRF1 targeting may hold therapeutic potential in vascular pathologies.
Keywords: Cardiovascular disease; Cell Biology; Epigenetics; Mouse models; Vascular Biology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
LXRα Promotes Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Formation Through UHRF1 Epigenetic Modification of miR-26b-3p.Circulation. 2024 Jul 2;150(1):30-46. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.123.065202. Epub 2024 Apr 1. Circulation. 2024. PMID: 38557060 Free PMC article.
-
Dickkopf-1 promotes Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell proliferation and migration through upregulating UHRF1 during Cyclic Stretch application.Int J Biol Sci. 2021 Mar 21;17(5):1234-1249. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.56247. eCollection 2021. Int J Biol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33867842 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-124 controls human vascular smooth muscle cell phenotypic switch via Sp1.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2017 Sep 1;313(3):H641-H649. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00660.2016. Epub 2017 Jun 30. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28667053
-
Smooth muscle cell-driven vascular diseases and molecular mechanisms of VSMC plasticity.Cell Signal. 2018 Dec;52:48-64. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2018.08.019. Epub 2018 Aug 30. Cell Signal. 2018. PMID: 30172025 Review.
-
Six Shades of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells Illuminated by KLF4 (Krüppel-Like Factor 4).Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2021 Nov;41(11):2693-2707. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.121.316600. Epub 2021 Sep 2. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2021. PMID: 34470477 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Reduced Platelet miR-223 Induction in Kawasaki Disease Leads to Severe Coronary Artery Pathology Through a miR-223/PDGFRβ Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Axis.Circ Res. 2020 Sep 11;127(7):855-873. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.316951. Epub 2020 Jun 29. Circ Res. 2020. PMID: 32597702 Free PMC article.
-
RNA Sequencing Analysis of Gene Expression by Electroacupuncture in Guinea Pig Gallstone Models.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Jan 7;2022:3793946. doi: 10.1155/2022/3793946. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35035504 Free PMC article.
-
UHRF1 Suppresses HIV-1 Transcription and Promotes HIV-1 Latency by Competing with p-TEFb for Ubiquitination-Proteasomal Degradation of Tat.mBio. 2021 Aug 31;12(4):e0162521. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01625-21. Epub 2021 Aug 31. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34465029 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Regulation of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotype Switching in Atherosclerotic Artery Remodeling: A Mini-Review.Front Genet. 2021 Aug 5;12:719456. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.719456. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34422021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of important genes related to HVSMC proliferation and migration in graft restenosis based on WGCNA.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 12;14(1):1237. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-51564-z. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38216708 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

