Function-Oriented Synthesis of Marine Phidianidine Derivatives as Potential PTP1B Inhibitors with Specific Selectivity
- PMID: 29558377
- PMCID: PMC5867641
- DOI: 10.3390/md16030097
Function-Oriented Synthesis of Marine Phidianidine Derivatives as Potential PTP1B Inhibitors with Specific Selectivity
Abstract
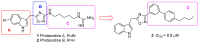
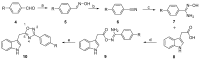
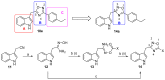
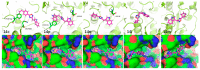
Phidianidines A and B are two novel marine indole alkaloids bearing an uncommon 1,2,4-oxadiazole ring and exhibiting various biological activities. Our previous research showed that the synthesized phidianidine analogs had the potential to inhibit the activity of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B), a validated target for Type II diabetes, which indicates that these analogs are worth further structural modification. Therefore, in this paper, a series of phidianidine derivatives were designed and rapidly synthesized with a function-oriented synthesis (FOS) strategy. Their inhibitory effects on PTP1B and T-cell protein tyrosine phosphatase (TCPTP) were evaluated, and several compounds displayed significant inhibitory potency and specific selectivity over PTP1B. The structure-activity relationship (SAR) and molecular docking analyses are also described.
Keywords: Function Oriented Synthesis; PTP1B inhibitor; docking analysis; marine natural products; phidianidine; specific selectivity; structure-activity relationship.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Design, synthesis and in vitro activity of phidianidine B derivatives as novel PTP1B inhibitors with specific selectivity.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2016 Feb 1;26(3):778-781. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2015.12.097. Epub 2015 Dec 29. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2016. PMID: 26774579
-
Discovery of novel high potent and cellular active ADC type PTP1B inhibitors with selectivity over TC-PTP via modification interacting with C site.Eur J Med Chem. 2018 Jan 20;144:692-700. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.12.064. Epub 2017 Dec 20. Eur J Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29289892
-
The design strategy of selective PTP1B inhibitors over TCPTP.Bioorg Med Chem. 2016 Aug 15;24(16):3343-52. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2016.06.035. Epub 2016 Jun 18. Bioorg Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 27353889 Review.
-
Canthinone alkaloids are novel protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitors.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2015 May 1;25(9):1979-81. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2015.03.014. Epub 2015 Mar 14. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2015. PMID: 25819098
-
The development of protein tyrosine phosphatase1B inhibitors defined by binding sites in crystalline complexes.Future Med Chem. 2018 Oct;10(19):2345-2367. doi: 10.4155/fmc-2018-0089. Future Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 30273014 Review.
Cited by
-
Phytochemical Content and Antidiabetic Properties of Most Commonly Used Antidiabetic Medicinal Plants of Kenya.Molecules. 2023 Oct 20;28(20):7202. doi: 10.3390/molecules28207202. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37894680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Re-engineering natural products to engage new biological targets.Nat Prod Rep. 2020 Nov 18;37(11):1395-1403. doi: 10.1039/d0np00059k. Nat Prod Rep. 2020. PMID: 33034322 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tobin J.F., Tam S. Recent advances in the development of small molecule inhibitors of PTP1B for the treatment of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Curr. Opin. Drug Discov. Dev. 2002;5:500–512. - PubMed
-
- Liu G., Trevillyan J.M. Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B as a target for the treatment of impaired glucose tolerance and type II diabetes. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs. 2002;3:1608–1616. - PubMed
-
- Elchebly M., Payette P., Michaliszyn E., Cromlish W., Collins S., Loy A.L., Normandin D., Cheng A., Himms-Hagen J., Chan C.C., et al. Increased insulin sensitivity and obesity resistance in mice lacking the protein tyrosine phosphatase-1B gene. Science. 1999;283:1544–1548. doi: 10.1126/science.283.5407.1544. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Klaman L.D., Boss O., Peroni O.D., Kim J.K., Martino J.L., Zabolotny J.M., Moghal N., Lubkin M., Kim Y.B., Sharpe A.H., et al. Increased energy expenditure, decreased adiposity, and tissue-specific insulin sensitivity in protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1B-deficient mice. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000;20:5479–5489. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.15.5479-5489.2000. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

