Targeting the Hippo Pathway and Cancer through the TEAD Family of Transcription Factors
- PMID: 29558384
- PMCID: PMC5876656
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers10030081
Targeting the Hippo Pathway and Cancer through the TEAD Family of Transcription Factors
Abstract
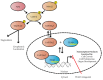
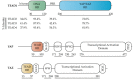
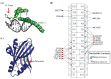
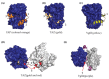
The Hippo pathway is a critical transcriptional signaling pathway that regulates cell growth, proliferation and organ development. The transcriptional enhanced associate domain (TEAD) protein family consists of four paralogous transcription factors that function to modulate gene expression in response to the Hippo signaling pathway. Transcriptional activation of these proteins occurs upon binding to the co-activator YAP/TAZ whose entry into the nucleus is regulated by Lats1/2 kinase. In recent years, it has become apparent that the dysregulation and/or overexpression of Hippo pathway effectors is implicated in a wide range of cancers, including prostate, gastric and liver cancer. A large body of work has been dedicated to understanding the therapeutic potential of modulating the phosphorylation and localization of YAP/TAZ. However, YAP/TAZ are considered to be natively unfolded and may be intractable as drug targets. Therefore, TEAD proteins present themselves as an excellent therapeutic target for intervention of the Hippo pathway. This review summarizes the functional role of TEAD proteins in cancer and assesses the therapeutic potential of antagonizing TEAD function in vivo.
Keywords: Hippo; TAZ; TEAD; YAP; cancer; transcription factor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare competing financial interests: all authors are employees of Genentech, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hippo pathway inhibition by blocking the YAP/TAZ-TEAD interface: a patent review.Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2018 Dec;28(12):867-873. doi: 10.1080/13543776.2018.1549226. Epub 2018 Dec 2. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2018. PMID: 30482112 Review.
-
Identification of Celastrol as a Novel YAP-TEAD Inhibitor for Cancer Therapy by High Throughput Screening with Ultrasensitive YAP/TAZ-TEAD Biosensors.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Oct 19;11(10):1596. doi: 10.3390/cancers11101596. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31635084 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Irreversible TEAD Inhibitor, SWTX-143, Blocks Hippo Pathway Transcriptional Output and Causes Tumor Regression in Preclinical Mesothelioma Models.Mol Cancer Ther. 2024 Jan 3;23(1):3-13. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-22-0681. Mol Cancer Ther. 2024. PMID: 37748190
-
Leveraging Hot Spots of TEAD-Coregulator Interactions in the Design of Direct Small Molecule Protein-Protein Interaction Disruptors Targeting Hippo Pathway Signaling.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Apr 13;16(4):583. doi: 10.3390/ph16040583. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37111340 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances of targeting the YAP/TAZ-TEAD complex in the hippo pathway for the treatment of cancers.Eur J Med Chem. 2022 Dec 15;244:114847. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114847. Epub 2022 Oct 13. Eur J Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 36265280 Review.
Cited by
-
Gene therapy for diffuse pleural mesotheliomas in preclinical models by concurrent expression of NF2 and SuperHippo.Cell Rep Med. 2024 Oct 15;5(10):101763. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101763. Epub 2024 Oct 4. Cell Rep Med. 2024. PMID: 39368484 Free PMC article.
-
TAZ promotes PDX1-mediated insulinogenesis.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022 Mar 13;79(3):186. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04216-2. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35279781 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial tissue geometry directs emergence of bioelectric field and pattern of proliferation.Mol Biol Cell. 2020 Jul 21;31(16):1691-1702. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E19-12-0719. Epub 2020 Jun 10. Mol Biol Cell. 2020. PMID: 32520653 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitors Targeting YAP in Gastric Cancer: Current Status and Future Perspectives.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021 Jun 9;15:2445-2456. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S308377. eCollection 2021. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021. PMID: 34140763 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Safety Considerations in the Development of Hippo Pathway Inhibitors in Cancers.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019 Aug 14;7:156. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2019.00156. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 31475147 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Galli G.G., Carrara M., Yuan W.C., Valdes-Quezada C., Gurung B., Pepe-Mooney B., Zhang T., Geeven G., Gray N.S., de Laat W., et al. YAP drives growth by controlling transcriptional pause release from dynamic enhancers. Mol. Cell. 2015;60:328–337. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.09.001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

