Therapeutic Properties and Biological Benefits of Marine-Derived Anticancer Peptides
- PMID: 29558431
- PMCID: PMC5877780
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19030919
Therapeutic Properties and Biological Benefits of Marine-Derived Anticancer Peptides
Abstract
Various organisms exist in the oceanic environment. These marine organisms provide an abundant source of potential medicines. Many marine peptides possess anticancer properties, some of which have been evaluated for treatment of human cancer in clinical trials. Marine anticancer peptides kill cancer cells through different mechanisms, such as apoptosis, disruption of the tubulin-microtubule balance, and inhibition of angiogenesis. Traditional chemotherapeutic agents have side effects and depress immune responses. Thus, the research and development of novel anticancer peptides with low toxicity to normal human cells and mechanisms of action capable of avoiding multi-drug resistance may provide a new method for anticancer treatment. This review provides useful information on the potential of marine anticancer peptides for human therapy.
Keywords: anticancer; antiproliferative; marine organism; peptide; therapeutic agents.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
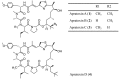
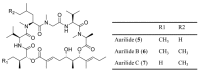
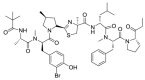
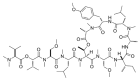
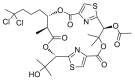
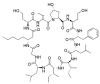
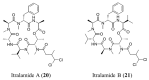
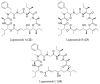

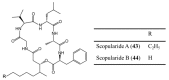
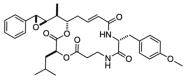
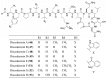
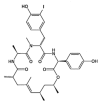
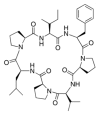
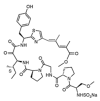
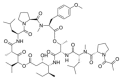
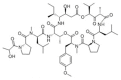
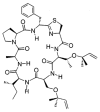
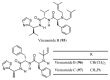
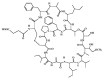
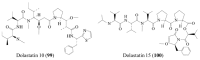

Similar articles
-
Bioactive peptides and depsipeptides with anticancer potential: sources from marine animals.Mar Drugs. 2012 May;10(5):963-986. doi: 10.3390/md10050963. Epub 2012 Apr 26. Mar Drugs. 2012. PMID: 22822350 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Marine Depsipeptides as Promising Pharmacotherapeutic Agents.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2017;18(1):72-91. doi: 10.2174/1389203717666160526122130. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2017. PMID: 27226199 Review.
-
Therapeutic Application of Diverse Marine-derived Natural Products in Cancer Therapy.Anticancer Res. 2019 Oct;39(10):5261-5284. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.13721. Anticancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31570422 Review.
-
Recent Progress of Marine Polypeptides as Anticancer Agents.Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2018;13(4):445-454. doi: 10.2174/1574892813666180430110033. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2018. PMID: 29708076 Review.
-
Marine Peptides as Anticancer Agents: A Remedy to Mankind by Nature.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2017;18(9):885-904. doi: 10.2174/1389203717666160724200849. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2017. PMID: 27455970 Review.
Cited by
-
Marine-Derived Compounds as Potential Inhibitors of Hsp90 for Anticancer and Antimicrobial Drug Development: A Comprehensive In Silico Study.Molecules. 2023 Dec 13;28(24):8074. doi: 10.3390/molecules28248074. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 38138564 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Anti-Cancer Peptides as Immunomodulatory Agents: Potential and Design Strategy.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Dec 1;14(12):2686. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14122686. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36559179 Free PMC article. Review.
-
On resin click-chemistry-mediated synthesis of novel enkephalin analogues with potent anti-nociceptive activity.Sci Rep. 2019 Apr 8;9(1):5771. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-42289-5. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30962495 Free PMC article.
-
Versatile Applications of Cyanobacteria in Biotechnology.Microorganisms. 2022 Nov 23;10(12):2318. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10122318. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36557571 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ascidian Toxins with Potential for Drug Development.Mar Drugs. 2018 May 13;16(5):162. doi: 10.3390/md16050162. Mar Drugs. 2018. PMID: 29757250 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lin X. Discovery of antitumor agents with peptides from marine sources. JSM Clin. Oncol. Res. 2014;2:1034.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

