The serum-based VeriStrat® test is associated with proinflammatory reactants and clinical outcome in non-small cell lung cancer patients
- PMID: 29558888
- PMCID: PMC5861613
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-018-4193-0
The serum-based VeriStrat® test is associated with proinflammatory reactants and clinical outcome in non-small cell lung cancer patients
Abstract
Background: The VeriStrat test is a serum proteomic signature originally discovered in non-responders to second line gefitinib treatment and subsequently used to predict differential benefit from erlotinib versus chemotherapy in previously treated advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Multiple studies highlight the clinical utility of the VeriStrat test, however, the mechanistic connection between VeriStrat-poor classification and poor prognosis in untreated and previously treated patients is still an active area of research. The aim of this study was to correlate VeriStrat status with other circulating biomarkers in advanced NSCLC patients - each with respect to clinical outcomes.
Methods: Serum samples were prospectively collected from 57 patients receiving salvage chemotherapy and 70 non-EGFR mutated patients receiving erlotinib. Patients were classified as either VeriStrat good or poor based on the VeriStrat test. Luminex immunoassays were used to measure circulating levels of 102 distinct biomarkers implicated in tumor aggressiveness and treatment resistance. A Cox PH model was used to evaluate associations between biomarker levels and clinical outcome, whereas the association of VeriStrat classifications with biomarker levels was assessed via the Mann-Whitney Rank Sum test.
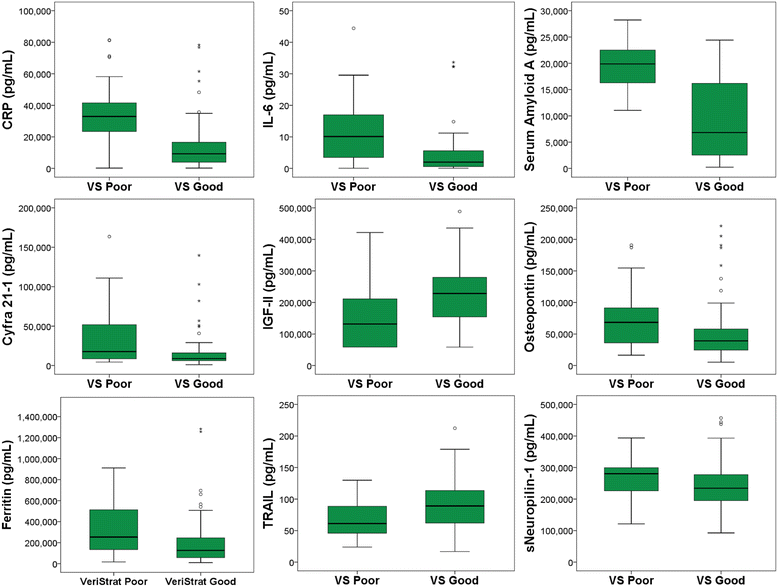
Results: VeriStrat was prognostic for outcome within the erlotinib treated patients (HR = 0.29, p < 0.0001) and predictive of differential treatment benefit between erlotinib and chemotherapy ((interaction HR = 0.25; interaction p = 0.0035). A total of 27 biomarkers out of 102 unique analytes were found to be significantly associated with OS (Cox PH p ≤ 0.05), whereas 16 biomarkers were found to be associated with PFS. Thrombospondin-2, C-reactive protein, TNF-receptor I, and placental growth factor were the analytes most highly associated with OS, all with Cox PH p-values ≤0.0001. VeriStrat status was found to be significantly associated with 23 circulating biomarkers (Mann-Whitney Rank Sum p ≤ 0.05), 6 of which had p < 0.001, including C-reactive protein, IL-6, serum amyloid A, CYFRA 21.1, IGF-II, osteopontin, and ferritin.
Conclusions: Strong associations were observed between survival and VeriStrat classifications as well as select circulating biomarkers associated with fibrosis, inflammation, and acute phase reactants as part of this study. The associations between these biomarkers and VeriStrat classification might have therapeutic implications for poor prognosis NSCLC patients, particularly with new immunotherapeutic treatment options.
Keywords: Biomarker; Erlotinib; Luminex; Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC); Serum; VeriStrat.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board at Rush University Medical Center and all specimens were collected with written informed consent from all subjects enrolled.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
All authors have no competing interests to disclose with exception of J.R., who is an employee at Biodesix, Incorporated.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Retrospective Assessment of a Serum Proteomic Test in a Phase III Study Comparing Erlotinib plus Placebo with Erlotinib plus Tivantinib (MARQUEE) in Previously Treated Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Oncologist. 2019 Jun;24(6):e251-e259. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2018-0089. Epub 2018 Aug 23. Oncologist. 2019. PMID: 30139835 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The clinical role of VeriStrat testing in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer considered unfit for first-line platinum-based chemotherapy.Eur J Cancer. 2019 Oct;120:86-96. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2019.07.025. Epub 2019 Sep 6. Eur J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31499384 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Prognostic and predictive role of the VeriStrat plasma test in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer treated with erlotinib or placebo in the NCIC Clinical Trials Group BR.21 trial.J Thorac Oncol. 2012 Nov;7(11):1653-60. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e31826c1155. J Thorac Oncol. 2012. PMID: 23059783 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of smoking status on progression-free and overall survival in non-small cell lung cancer patients receiving erlotinib or gefitinib: a meta-analysis.J Clin Pharm Ther. 2015 Dec;40(6):661-71. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.12332. Epub 2015 Nov 17. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2015. PMID: 26573867
-
[Current status of erlotinib and gefitinib in palliative therapy for NSCLC--does the EGF-R mutation state have any significance?].Pneumologie. 2010 Dec;64(12):727-35. doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1255532. Epub 2010 Jun 24. Pneumologie. 2010. PMID: 20577948 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Role of mass spectrometry-based serum proteomics signatures in predicting clinical outcomes and toxicity in patients with cancer treated with immunotherapy.J Immunother Cancer. 2022 Mar;10(3):e003566. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2021-003566. J Immunother Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35347071 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Comprehensive Review of Protein Biomarkers for Invasive Lung Cancer.Curr Oncol. 2024 Aug 23;31(9):4818-4854. doi: 10.3390/curroncol31090360. Curr Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39329988 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review on trends in development and translation of omics signatures in cancer.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2024 Feb 3;23:954-971. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2024.01.024. eCollection 2024 Dec. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2024. PMID: 38385061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Prediction Of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutation And Prognosis Of EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor By Serum Ferritin In Advanced NSCLC.Cancer Manag Res. 2019 Oct 7;11:8835-8843. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S216037. eCollection 2019. Cancer Manag Res. 2019. PMID: 31632143 Free PMC article.
-
Mass Spectrometry-Based Multivariate Proteomic Tests for Prediction of Outcomes on Immune Checkpoint Blockade Therapy: The Modern Analytical Approach.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jan 28;21(3):838. doi: 10.3390/ijms21030838. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32012941 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Taguchi F, Solomon B, Gregorc V, Roder H, Gray R, Kasahara K, Nishio M, Brahmer J, Spreafico A, Ludovini V, et al. Mass spectrometry to classify non-small-cell lung cancer patients for clinical outcome after treatment with epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors: a multicohort cross-institutional study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2007;99(11):838–846. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djk195. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Amann JM, Lee JW, Roder H, Brahmer J, Gonzalez A, Schiller JH, Carbone DP. Genetic and proteomic features associated with survival after treatment with erlotinib in first-line therapy of non-small cell lung cancer in eastern cooperative oncology group 3503. J Thorac Oncol. 2010;5(2):169–178. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181c8cbd9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Carbone DP, Ding K, Roder H, Grigorieva J, Roder J, Tsao MS, Seymour L, Shepherd FA. Prognostic and predictive role of the VeriStrat plasma test in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer treated with erlotinib or placebo in the NCIC clinical trials group BR.21 trial. J Thorac Oncol. 2012;7(11):1653–1660. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e31826c1155. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wakelee H, Goldman JW, Gadgeel S, Camidge DR, Reckamp KL, Ou SI, Yu HA, Solomon B, Liu SV, Perol M, et al. PS01.66: biomarker stratification of outcomes of third-generation EGFR TKI therapy in patients with previously-treated advanced NSCLC: Topic: Medical Oncology. J Thorac Oncol. 2016;11(11S):S311–S312. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2016.09.101. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous