Effect of number and position of intraocular lens haptics on anterior capsule contraction: a randomized, prospective trial
- PMID: 29558909
- PMCID: PMC5859398
- DOI: 10.1186/s12886-018-0742-1
Effect of number and position of intraocular lens haptics on anterior capsule contraction: a randomized, prospective trial
Abstract
Background: The present study aimed to evaluate the degree of anterior capsule contraction (capsulorhexis contraction) with three different single-piece, hydrophilic acrylic intraocular lenses (IOLs).
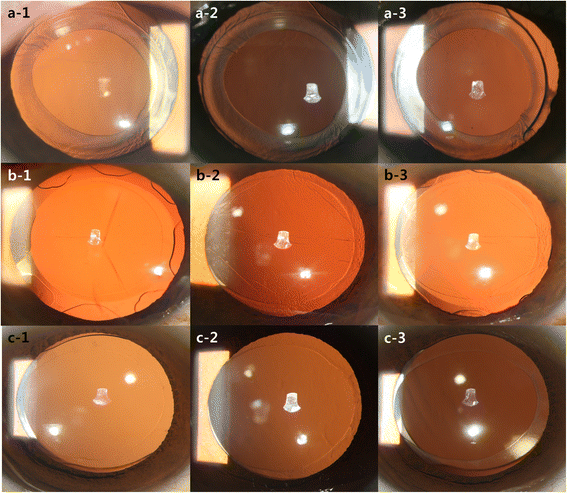
Methods: Patients were prospectively randomized to be implanted with one of three types of IOLs during cataract surgery: the Ophtec Precizon (IOL A), the Lucid Korea Microflex (IOL B), and the Carl Zeiss Asphina (IOL C). One week, 2 weeks, and 6 months after surgery, the area of the anterior capsule opening was measured using digital retro-illumination images after dilation of the pupil. The data were then evaluated using POCOman software.
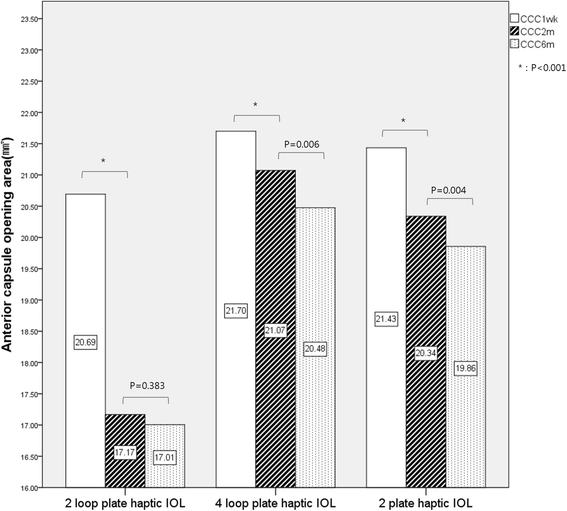
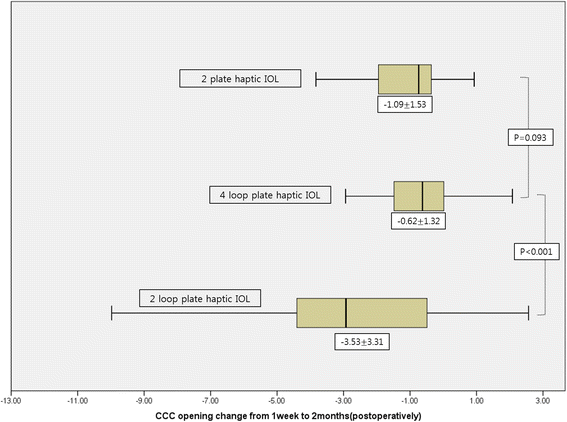
Results: The study included 236 eyes of 202 patients. The area of the anterior capsule opening reduced by 3.53 ± 3.31 mm (17.06% ± 15.99%) between 1 week and 2 months post-operatively in the IOL A group, by 0.62 ± 1.32 mm (2.87% ± 6.03%) in the IOL B group, and by 1.09 ± 1.53 mm (4.72% ± 6.10%) in the IOL C group. The IOL B group showed minimal anterior capsule contraction 2 months after surgery (p < 0.001).
Conclusions: IOLs with a four-plate haptic design (IOL B) showed more anterior capsular stability than those with a two-loop plate haptic (IOL A) or two-plate haptic (IOL C) design. The number and position of haptics in a capsular bag may affect anterior capsule contraction. We assume that supporting the zonules evenly may play a role in anterior capsular stability.
Trial registration: Current Controlled Trials ISRCTN76566080 , Retrospectively registered (Date of registration: 14 Feb 2018).
Keywords: Anterior capsule contraction syndrome; Anterior capsule of the lens; Capsulorhexis; Cataract surgery; Intraocular lens.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Approval for the present study was obtained from the Ethics Committee of the Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital (Korea). All patients were informed about the study prior to enrollment and signed an informed consent, in accordance with the tenets of the Helsinki Declaration.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

