The Association of Frailty With Post-ICU Disability, Nursing Home Admission, and Mortality: A Longitudinal Study
- PMID: 29559308
- PMCID: PMC6026287
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chest.2018.03.007
The Association of Frailty With Post-ICU Disability, Nursing Home Admission, and Mortality: A Longitudinal Study
Abstract
Background: Frailty is a strong indicator of vulnerability among older persons, but its association with ICU outcomes has not been evaluated prospectively (ie, with objective measurements obtained prior to ICU admission). Our objective was to prospectively evaluate the relationship between frailty and post-ICU disability, incident nursing home admission, and death.
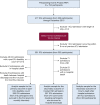
Methods: The parent cohort included 754 adults aged ≥ 70 years, who were evaluated monthly for disability in 13 functional activities and every 18 months for frailty (1998-2014). Frailty was assessed using the Fried index, where frailty, prefrailty, and nonfrailty were defined, respectively, as at least three, one or two, and zero criteria (of five). The analytic sample included 391 ICU admissions.
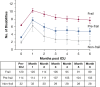
Results: The mean age was 84.0 years. Frailty and prefrailty were present prior to 213 (54.5%) and 140 (35.8%) of the 391 admissions, respectively. Relative to nonfrailty, frailty was associated with 41% greater disability over the 6 months following a critical illness (adjusted risk ratio, 1.41; 95% CI, 1.12-1.78); prefrailty conferred 28% greater disability (adjusted risk ratio, 1.28; 95% CI, 1.01-1.63). Frailty (odds ratio, 3.52; 95% CI, 1.23-10.08), but not prefrailty (odds ratio, 2.01; 95% CI, 0.77-5.24), was associated with increased nursing home admission. Each one-point increase in frailty count (range, 0-5) was associated with double the likelihood of death (hazard ratio, 2.00; 95% CI, 1.33-3.00) through 6 months of follow-up.
Conclusions: Pre-ICU frailty status was associated with increased post-ICU disability and new nursing home admission among ICU survivors, and death among all admissions. Pre-ICU frailty status may provide prognostic information about outcomes after a critical illness.
Keywords: aging; critical care; disability; epidemiology.
Copyright © 2018 American College of Chest Physicians. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Comment in
-
Beyond the ICU: Frailty and Post-ICU Disability. Healthcare Use after Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and Severe Sepsis.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019 Apr 15;199(8):1028-1030. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201805-0928RR. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019. PMID: 30849230 No abstract available.
References
-
- Administration on Aging, Administration for Community Living, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. A profile of older Americans: 2015. https://www.acl.gov/sites/default/files/Aging%20and%20Disability%20in%20.... Accessed February 8, 2017.
-
- Angus D.C., Kelley M.A., Schmitz R.J., White A., Popovich J., Jr., Committee on Manpower for Pulmonary and Critical Care Societies (COMPACCS) Current and projected workforce requirements for care of the critically ill and patients with pulmonary disease: can we meet the requirements of an aging population? JAMA. 2000;284(21):2762–2770. - PubMed
-
- Fried L.P., Guralnik J.M. Disability in older adults: evidence regarding significance, etiology, and risk. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1997;45(1):92–100. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

