Symptom Prioritization among Adults Receiving In-Center Hemodialysis: A Mixed Methods Study
- PMID: 29559445
- PMCID: PMC5969481
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.10850917
Symptom Prioritization among Adults Receiving In-Center Hemodialysis: A Mixed Methods Study
Abstract
Background and objectives: Individuals receiving in-center hemodialysis experience a high symptom burden that detrimentally affects their quality of life. There are few evidence-based interventions for symptom relief in this population. To stimulate innovation in symptom management, data on patient symptom prioritization and treatment preferences are needed. We undertook this study to (1) identify patient-prioritized symptoms for the development of symptom relief therapies and (2) elicit preferences for treatments among individuals receiving hemodialysis.
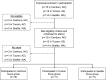
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: We conducted a mixed methods study that included focus groups in Carrboro, North Carolina; Tucson, Arizona; and Seattle, Washington and a nationally distributed online survey. Focus group transcripts were analyzed for patterns, and the highest priority symptoms were determined on the basis of frequency and report severity. We used focus group findings to inform survey items. Focus group and survey results were crossvalidated and synthesized for final symptom prioritization.
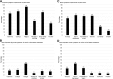
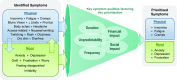
Results: There were 32 participants across three focus groups and 87 survey respondents from 27 states in the United States. The physical symptoms of insomnia, fatigue, muscle cramping, and nausea/vomiting and the mood symptoms of anxiety and depressed mood were reported by participants in all focus groups. Among survey respondents, fatigue (94%), cramping (79%), and body aches (76%) were the most common physical symptoms, and feeling depressed (66%), worried (64%), and frustrated (63%) were the most common mood symptoms. The top-prioritized symptoms were consistent across focus group and survey participants and included the physical symptoms insomnia, fatigue, and cramping and the mood symptoms anxiety, depression, and frustration. Participants indicated that symptom frequency, duration, unpredictability, and social and financial effects factored most heavily into symptom prioritization.
Conclusions: Patients prioritized the physical symptoms of insomnia, fatigue, and cramping and the mood symptoms of anxiety, depression, and frustration as the top symptoms for which to find new therapies.
Keywords: Anxiety; ESRD; Emotions; Fatigue; Focus Groups; Frustration; Nausea; Pain; Sleep Initiation and Maintenance Disorders; Surveys and Questionnaires; Vomiting; chronic dialysis; depression; dialysis; end-stage renal disease; hemodialysis; quality of life; renal dialysis.
Copyright © 2018 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures


References
-
- Saran R, Robinson B, Abbott KC, Agodoa LY, Albertus P, Ayanian J, Balkrishnan R, Bragg-Gresham J, Cao J, Chen JL, Cope E, Dharmarajan S, Dietrich X, Eckard A, Eggers PW, Gaber C, Gillen D, Gipson D, Gu H, Hailpern SM, Hall YN, Han Y, He K, Hebert H, Helmuth M, Herman W, Heung M, Hutton D, Jacobsen SJ, Ji N, Jin Y, Kalantar-Zadeh K, Kapke A, Katz R, Kovesdy CP, Kurtz V, Lavalee D, Li Y, Lu Y, McCullough K, Molnar MZ, Montez-Rath M, Morgenstern H, Mu Q, Mukhopadhyay P, Nallamothu B, Nguyen DV, Norris KC, O'Hare AM, Obi Y, Pearson J, Pisoni R, Plattner B, Port FK, Potukuchi P, Rao P, Ratkowiak K, Ravel V, Ray D, Rhee CM, Schaubel DE, Selewski DT, Shaw S, Shi J, Shieu M, Sim JJ, Song P, Soohoo M, Steffick D, Streja E, Tamura MK, Tentori F, Tilea A, Tong L, Turf M, Wang D, Wang M, Woodside K, Wyncott A, Xin X, Zang W, Zepel L, Zhang S, Zho H, Hirth RA, Shahinian V: US renal data system 2016 annual data report: Epidemiology of kidney disease in the United States. Am J Kidney Dis 69[Suppl 1]: A7–A8, 2017 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Merkus MP, Jager KJ, Dekker FW, de Haan RJ, Boeschoten EW, Krediet RT: Physical symptoms and quality of life in patients on chronic dialysis: Results of The Netherlands Cooperative Study on Adequacy of Dialysis (NECOSAD). Nephrol Dial Transplant 14: 1163–1170, 1999 - PubMed
-
- Valderrábano F, Jofre R, López-Gómez JM: Quality of life in end-stage renal disease patients. Am J Kidney Dis 38: 443–464, 2001 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

