The balance of interleukin (IL)-6, IL-6·soluble IL-6 receptor (sIL-6R), and IL-6·sIL-6R·sgp130 complexes allows simultaneous classic and trans-signaling
- PMID: 29559558
- PMCID: PMC5936821
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA117.001163
The balance of interleukin (IL)-6, IL-6·soluble IL-6 receptor (sIL-6R), and IL-6·sIL-6R·sgp130 complexes allows simultaneous classic and trans-signaling
Abstract
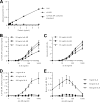
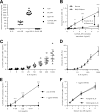
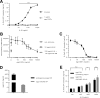
Interleukin (IL-)6 is the major pro-inflammatory cytokine within the IL-6 family. IL-6 signals via glycoprotein 130 (gp130) and the membrane-bound or soluble IL-6 receptor (IL-6R), referred to as classic or trans-signaling, respectively. Whereas inflammation triggers IL-6 expression, eventually rising to nanogram/ml serum levels, soluble IL-6R (sIL-6R) and soluble gp130 (sgp130) are constitutively present in the upper nanogram/ml range. Calculations based on intermolecular affinities have suggested that systemic IL-6 is immediately trapped in IL-6·sIL-6R and IL-6·sIL-6R·sgp130 complexes, indicating that sIL-6R and sgp130 constitute a buffer system that increases the serum half-life of IL-6 or restricts systemic IL-6 signaling. However, this scenario has not been experimentally validated. Here, we quantified IL-6·sIL-6R and IL-6·sIL-6R·sgp130 complexes over a wide concentration range. The amounts of IL-6 used in this study reflect concentrations found during active inflammatory events. Our results indicated that most IL-6 is free and not complexed with sIL-6R or sgp130, indicating that the level of endogenous sgp130 in the bloodstream is not sufficient to block IL-6 trans-signaling via sIL-6R. Importantly, addition of the single-domain antibody VHH6, which specifically stabilizes IL-6·sIL-6R complexes but did not bind to IL-6 or sIL-6R alone, drove free IL-6 into IL-6·sIL-6R complexes and boosted trans-signaling but not classic signaling, demonstrating that endogenous sIL-6R has at least the potential to form complexes with IL-6. Our findings indicate that even though high concentrations of sIL-6R and sgp130 are present in human serum, the relative ratio of free IL-6 to IL-6·sIL-6R allows for simultaneous classic and trans-signaling.
Keywords: Trans-signaling; classic signaling; cytokine; glycoprotein; interleukin 6 (IL-6); interleukin 6 receptor (IL6R); signal transduction.
© 2018 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
G. H. W. is employed by CONARIS Research Institute AG (Kiel, Germany), which is commercially developing sgp130Fc proteins as therapeutics for inflammatory diseases
Figures


References
-
- Horiuchi S., Koyanagi Y., Zhou Y., Miyamoto H., Tanaka Y., Waki M., Matsumoto A., Yamamoto M., and Yamamoto N. (1994) Soluble interleukin-6 receptors released from T cell or granulocyte/macrophage cell lines and human peripheral blood mononuclear cells are generated through an alternative splicing mechanism. Eur. J. Immunol. 24, 1945–1948 10.1002/eji.1830240837 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Matthews V., Schuster B., Schütze S., Bussmeyer I., Ludwig A., Hundhausen C., Sadowski T., Saftig P., Hartmann D., Kallen K.-J., and Rose-John S. (2003) Cellular cholesterol depletion triggers shedding of the human interleukin-6 receptor by ADAM10 and ADAM17 (TACE). J. Biol. Chem. 278, 38829–38839 10.1074/jbc.M210584200 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

