Type I interferon in rheumatic diseases
- PMID: 29559718
- PMCID: PMC6625751
- DOI: 10.1038/nrrheum.2018.31
Type I interferon in rheumatic diseases
Abstract
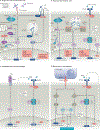
The type I interferon pathway has been implicated in the pathogenesis of a number of rheumatic diseases, including systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjögren syndrome, myositis, systemic sclerosis, and rheumatoid arthritis. In normal immune responses, type I interferons have a critical role in the defence against viruses, yet in many rheumatic diseases, large subgroups of patients demonstrate persistent activation of the type I interferon pathway. Genetic variations in type I interferon-related genes are risk factors for some rheumatic diseases, and can explain some of the heterogeneity in type I interferon responses seen between patients within a given disease. Inappropriate activation of the immune response via Toll-like receptors and other nucleic acid sensors also contributes to the dysregulation of the type I interferon pathway in a number of rheumatic diseases. Theoretically, differences in type I interferon activity between patients might predict response to immune-based therapies, as has been demonstrated for rheumatoid arthritis. A number of type I interferon and type I interferon pathway blocking therapies are currently in clinical trials, the results of which are promising thus far. This Review provides an overview of the many ways in which the type I interferon system affects rheumatic diseases.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

