Transmembrane TNF-alpha promotes chemoresistance in breast cancer cells
- PMID: 29559745
- PMCID: PMC6013421
- DOI: 10.1038/s41388-018-0221-4
Transmembrane TNF-alpha promotes chemoresistance in breast cancer cells
Abstract
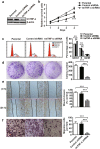
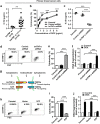
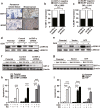
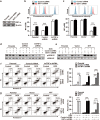
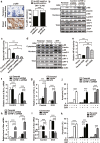
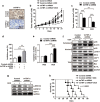
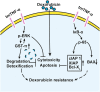
Chemoresistance remains a major obstacle to successful treatment of breast cancer. Although soluble tumor necrosis factor-α (sTNF-α) has been implicated in mediating drug-resistance in human cancers, whether transmembrane tumor necrosis factor-α (tmTNF-α) plays a role in chemoresistance remains unclear. Here we found that over 50% of studied patients expressed tmTNF-α at high levels in breast cancer tissues and tmTNF-α expression positively correlated with resistance to anthracycline chemotherapy. Alteration of tmTNF-α expression changed the sensitivity of primary human breast cancer cells and breast cancer cell lines to doxorubicin (DOX). Overexpression of N-terminal fragment (NTF) of tmTNF-α, a mutant form with intact intracellular domain of tmTNF-α to transmit reverse signals, induced DOX-resistance. Mechanistically, the tmTNF-α/NTF-ERK-GST-π axis and tmTNF-α/NTF-NF-κB-mediated anti-apoptotic functions were required for tmTNF-α-induced DOX-resistance. In a xenograft mouse model, the combination of tmTNF-α suppression with chemotherapy significantly enhanced the efficacy of DOX. Our data indicate that tmTNF-α mediates DOX-resistance through reverse signaling and targeting tmTNF-α may be beneficial for the treatment of DOX-resistant breast cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Arcamone F, Cassinelli G, Fantini G, Grein A, Orezzi P, Pol C, et al. Adriamycin, 14-hydroxydaunomycin, a new antitumor antibiotic from S. peucetius var. caesius. Reprinted from Biotechnology and Bioengineering, Vol. XI, Issue 6, Pages 1101–1110 (1969) Biotechnol Bioeng. 2000;67:704–13. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0290(20000320)67:6<704::AID-BIT8>3.0.CO;2-L. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mackey JR, Martin M, Pienkowski T, Rolski J, Guastalla JP, Sami A, et al. Adjuvant docetaxel, doxorubicin, and cyclophosphamide in node-positive breast cancer: 10-year follow-up of the phase 3 randomised BCIRG 001 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2013;14:72–80. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(12)70525-9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Martin M, Ruiz A, Ruiz Borrego M, Barnadas A, Gonzalez S, Calvo L, et al. Fluorouracil, doxorubicin, and cyclophosphamide (FAC) versus FAC followed by weekly paclitaxel as adjuvant therapy for high-risk, node-negative breast cancer: results from the GEICAM/2003-02 study. J Clin Oncol: Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2013;31:2593–9. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2012.46.9841. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dalpiaz O, al Rabi N, Galfano A, Martignoni G, Ficarra V, Artibani W. Small cell carcinoma of the bladder: a case report and a literature review. Arch Esp Urol. 2003;56:197–202. - PubMed
-
- Filipits M, Pohl G, Stranzl T, Kaufmann H, Ackermann J, Gisslinger H, et al. Low p27Kip1 expression is an independent adverse prognostic factor in patients with multiple myeloma. Clin Cancer Res: Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res. 2003;9:820–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

