Can dexmedetomidine reduce atrial fibrillation after cardiac surgery? A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 29559768
- PMCID: PMC5856293
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S153834
Can dexmedetomidine reduce atrial fibrillation after cardiac surgery? A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Purpose: Cardiac surgery patients always present with atrial fibrillation (AF) after admission to the intensive care unit, leading to high mortality and lengthy hospitalization. Dexmedetomidine (DEX) is a popular medication used for sedation in the intensive care unit; however, whether it can reduce AF needs to be analyzed.
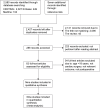
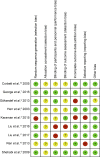
Materials and methods: Three primary databases, Medline, Embase (Ovid SP) and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), were searched. All English language and randomized control designed clinical publications comparing DEX to control medicines for sedation after elective cardiac surgery were included. Two independent colleagues conducted the data extraction and quality assessments. The subgroup analysis was performed according to the medicine used, age, AF history, and whether previous beta-blocker premedication and cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) were applied. The overall incidence of AF was analyzed.
Results: A total of 1,295 patients in nine studies met the selection criteria among 2,587 studies screened from the database. After quantitative synthesis, our results revealed that the DEX group was not associated with a decreased incidence of AF compared with the placebo (risk ratio [RR] 0.76, 95% CI 0.37, 1.55, P=0.44) and morphine groups (RR 0.86, 95% CI 0.56, 1.31, P=0.48). Subgroup analysis also indicated that the DEX vs propofol comparison exhibited no difference: 1) for patients of age >60 years (P=0.69) or ≤60 years (P=0.69); 2) under CPB surgery (P=0.45) or without CPB surgery (P=0.88); 3) with beta-blocker premedication (P=0.32) or without beta-blocker premedication (P=0.90); and 4) with AF history (RR 1.07, 95% CI 0.85, 1.36, P=0.57) or without AF history (P=0.30).
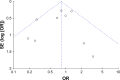
Conclusion: This meta-analysis revealed that DEX could not reduce the incidence of AF compared to control medicines following cardiac surgery. DEX may have an increased influence on AF occurrence if patients had a history of AF. However, cautious interpretation should be made due to high clinical heterogeneity.
Keywords: atrial fibrillation; cardiac surgery; dexmedetomidine; sedation.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

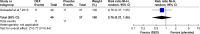
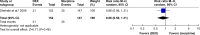

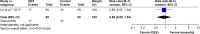
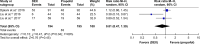



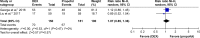
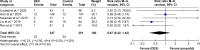
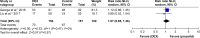

References
-
- Worden JC, Asare K. Postoperative atrial fibrillation: role of inflammatory biomarkers and use of colchicine for its prevention. Pharmacotherapy. 2014;34(11):1167–1173. - PubMed
-
- Ommen SR, Odell JA, Stanton MS. Atrial arrhythmias after cardiothoracic surgery. N Engl J Med. 1997;336(20):1429–1434. - PubMed
-
- Banach M, Kourliouros A, Reinhart KM, et al. Postoperative atrial fibrillation – What do we really know? Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2010;8(4):553–572. - PubMed
-
- Karaman Y, Abud B, Tekgul ZT, Cakmak M, Yildiz M, Gonullu M. Effects of dexmedetomidine and propofol on sedation in patients after coronary artery bypass graft surgery in a fast-track recovery room setting. J Anesth. 2015;29(4):522–528. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

