Liposome-Encapsulated Baicalein Suppressed Lipogenesis and Extracellular Matrix Formation in Hs68 Human Dermal Fibroblasts
- PMID: 29559910
- PMCID: PMC5845745
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00155
Liposome-Encapsulated Baicalein Suppressed Lipogenesis and Extracellular Matrix Formation in Hs68 Human Dermal Fibroblasts
Abstract
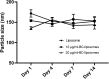
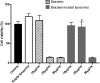
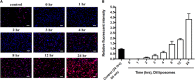
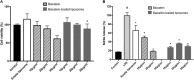
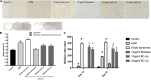
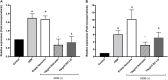
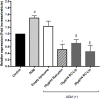
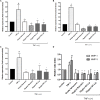
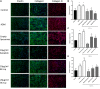
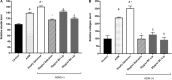
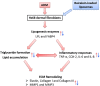
The dermis of human skin contains large numbers of fibroblasts that are responsible for the production of the extracellular matrix (ECM) that supporting skin integrity, elasticity and wound healing. Previously, an in vivo study demonstrated that dermal fibroblasts siting in the lower dermis are capable to convert into skin adipose layer and hence fibroblast lipogenesis may vary the structure and elasticity of dermis. In the present study, Hs68 human dermal fibroblasts were utilized as an in vitro model to study the lipogenesis via using adipogenic differentiation medium (ADM). Baicalein, isolated from Scutellaria baicalensis, is one of the flavonoids to inhibit adipocyte differentiation due to high antioxidant activity in vitro. In order to develop a suitable formulation for baicalein (a poorly water-soluble drug), soybean phosphatidylcholine (SPC) was used to prepare baicalein-loaded liposomes to enhance drug bioavailability. Our results demonstrated that liposome-encapsulated baicalein protected cell viability and increased cellular uptake efficiency of Hs68 fibroblasts. Lipid accumulation, triglyceride synthesis and gene expressions of lipogenesis enzymes (FABP4 and LPL) were significantly increased in ADM-stimulated Hs68 fibroblasts but subsequently suppressed by liposome-encapsulated baicalein. In addition, ADM-induced TNF-α expression and related inflammatory factors was down-regulated by liposome-encapsulated baicalein. Through ADM-induced lipogenesis, the protein expression of elastin, type I and type III collagens increased remarkably, whereas liposome-encapsulated baicalein can down-regulate ADM-induced ECM protein synthesis. Taken together, we found that liposome-encapsulated baicalein can inhibit ADM-induced lipid accumulation and ECM formation in Hs68 fibroblasts through the suppression of lipogenesis enzymes and inflammatory responses. Liposome-encapsulated baicalein may have the potential to improve wound healing and restore skin structure after skin injury.
Keywords: Hs68 human dermal fibroblast; adipogenic differentiation medium; baicalein; lipogenesis; liposomes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dermal Lipogenesis Inhibits Adiponectin Production in Human Dermal Fibroblasts while Exogenous Adiponectin Administration Prevents against UVA-Induced Dermal Matrix Degradation in Human Skin.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Jul 14;17(7):1129. doi: 10.3390/ijms17071129. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27428951 Free PMC article.
-
Altered proliferative responses of dermal fibroblasts to TGF-beta1 may contribute to chronic venous stasis ulcer.J Vasc Surg. 2003 Jun;37(6):1285-93. doi: 10.1016/s0741-5214(02)75295-6. J Vasc Surg. 2003. PMID: 12764277
-
7,8-Dihydroxyflavone attenuates TNF-α-induced skin aging in Hs68 human dermal fibroblast cells via down-regulation of the MAPKs/Akt signaling pathways.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Nov;95:1580-1587. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.09.098. Epub 2017 Oct 6. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28950658
-
Matrix-directed differentiation of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells to dermal-like fibroblasts that produce extracellular matrix.J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2016 Oct;10(10):E546-E558. doi: 10.1002/term.1865. Epub 2014 Feb 25. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2016. PMID: 24616295
-
Compound K inhibits MMP-1 expression through suppression of c-Src-dependent ERK activation in TNF-α-stimulated dermal fibroblast.Exp Dermatol. 2014 Nov;23(11):819-24. doi: 10.1111/exd.12536. Epub 2014 Oct 1. Exp Dermatol. 2014. PMID: 25181017
Cited by
-
Novel Liposomal Formulation of Baicalein for the Treatment of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: Design, Characterization, and Evaluation.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jan 4;15(1):179. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15010179. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36678808 Free PMC article.
-
Self-Emulsifying Phospholipid Preconcentrates for the Enhanced Photoprotection of Luteolin.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Sep 7;14(9):1896. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14091896. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36145644 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Astaxanthin-Loaded Nanosized Liposomal Formulation to Improve Bone Health.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Apr 18;15(4):490. doi: 10.3390/ph15040490. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35455487 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Caveolin-1 for enhanced rotator cuff repair: findings from single-cell RNA sequencing.Cell Death Discov. 2025 Mar 5;11(1):88. doi: 10.1038/s41420-025-02359-2. Cell Death Discov. 2025. PMID: 40044676 Free PMC article.
-
The potential of functionalized dressing releasing flavonoids facilitates scar-free healing.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Oct 3;9:978120. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.978120. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36262272 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ambele M. A., Dessels C., Durandt C., Pepper M. S. (2016). Genome-wide analysis of gene expression during adipogenesis in human adipose-derived stromal cells reveals novel patterns of gene expression during adipocyte differentiation. Stem Cell Res. 16 725–734. 10.1016/j.scr.2016.04.011 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

