Heritability and Genome-Wide Association Analyses of Serum Uric Acid in Middle and Old-Aged Chinese Twins
- PMID: 29559957
- PMCID: PMC5845532
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00075
Heritability and Genome-Wide Association Analyses of Serum Uric Acid in Middle and Old-Aged Chinese Twins
Abstract
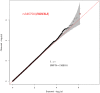
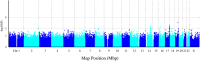
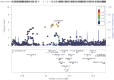
Serum uric acid (SUA), as the end product of purine metabolism, has proven emerging roles in human disorders. Here based on a sample of 379 middle and old-aged Chinese twin pairs, we aimed to explore the magnitude of genetic impact on SUA variation by performing sex-limitation twin modeling analyses and further detect specific genetic variants related to SUA by conducting a genome-wide association study. Monozygotic (MZ) twin correlation for SUA level (rMZ = 0.56) was larger than for dizygotic (DZ) twin correlation (rDZ = 0.39). The common effects sex-limitation model provided the best fit with additive genetic parameter (A) accounting for 46.3%, common or shared environmental parameter (C) accounting for 26.3% and unique/nonshared environmental parameter (E) accounting for 27.5% for females and 29.9, 33.1, and 37.0% for males, respectively. Although no SUA-related genetic variants reached genome-wide significance level, 25 SNPs were suggestive of association (P < 1 × 10-5). Most of the SNPs were located in an intronic region and detected to have regulatory effects on gene transcription. The cell-type specific enhancer of skeletal muscle was detected which has been reported to implicate SUA. Two promising genetic regions on chromosome 17 around rs2253277 and chromosome 14 around rs11621523 were found. Gene-based analysis found 167 genes nominally associated with SUA level (P < 0.05), including PTGR2, ENTPD5, well-known SLC2A9, etc. Enrichment analysis identified one pathway of transmembrane transport of small molecules and 20 GO gene sets involving in ion transport, transmembrane transporter activity, hydrolase activity acting on acid anhydrides, etc. In conclusion, SUA shows moderate heritability in women and low heritability in men in the Chinese population and genetic variations are significantly involved in functional genes and regulatory domains that mediate SUA level. Our findings provide clues to further elucidate molecular physiology of SUA homeostasis and identify new diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets for hyperuricemia and gout.
Keywords: Chinese twins; gene-based test; genome-wide association study; heritability; serum uric acid.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

