Griffin: A Tool for Symbolic Inference of Synchronous Boolean Molecular Networks
- PMID: 29559993
- PMCID: PMC5845696
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2018.00039
Griffin: A Tool for Symbolic Inference of Synchronous Boolean Molecular Networks
Abstract
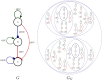
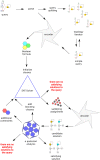
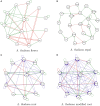
Boolean networks are important models of biochemical systems, located at the high end of the abstraction spectrum. A number of Boolean gene networks have been inferred following essentially the same method. Such a method first considers experimental data for a typically underdetermined "regulation" graph. Next, Boolean networks are inferred by using biological constraints to narrow the search space, such as a desired set of (fixed-point or cyclic) attractors. We describe Griffin, a computer tool enhancing this method. Griffin incorporates a number of well-established algorithms, such as Dubrova and Teslenko's algorithm for finding attractors in synchronous Boolean networks. In addition, a formal definition of regulation allows Griffin to employ "symbolic" techniques, able to represent both large sets of network states and Boolean constraints. We observe that when the set of attractors is required to be an exact set, prohibiting additional attractors, a naive Boolean coding of this constraint may be unfeasible. Such cases may be intractable even with symbolic methods, as the number of Boolean constraints may be astronomically large. To overcome this problem, we employ an Artificial Intelligence technique known as "clause learning" considerably increasing Griffin's scalability. Without clause learning only toy examples prohibiting additional attractors are solvable: only one out of seven queries reported here is answered. With clause learning, by contrast, all seven queries are answered. We illustrate Griffin with three case studies drawn from the Arabidopsis thaliana literature. Griffin is available at: http://turing.iimas.unam.mx/griffin.
Keywords: Boolean networks; Boolean satisfiability problem; attractors; biological constraints; clause learning; model inference; molecular networks.
Figures



Similar articles
-
An efficient algorithm for computing fixed length attractors based on bounded model checking in synchronous Boolean networks with biochemical applications.Genet Mol Res. 2015 Apr 28;14(2):4238-44. doi: 10.4238/2015.April.28.5. Genet Mol Res. 2015. PMID: 25966195
-
An efficient algorithm for computing attractors of synchronous and asynchronous Boolean networks.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 9;8(4):e60593. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060593. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23585840 Free PMC article.
-
A SAT-based algorithm for finding attractors in synchronous Boolean networks.IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 2011 Sep-Oct;8(5):1393-9. doi: 10.1109/TCBB.2010.20. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 2011. PMID: 21778527
-
Inference of gene regulatory networks using boolean-network inference methods.J Bioinform Comput Biol. 2009 Dec;7(6):1013-29. doi: 10.1142/s0219720009004448. J Bioinform Comput Biol. 2009. PMID: 20014476 Review.
-
Review and assessment of Boolean approaches for inference of gene regulatory networks.Heliyon. 2022 Aug 9;8(8):e10222. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10222. eCollection 2022 Aug. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36033302 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in modeling cellular state dynamics: integrating omics data and predictive techniques.Anim Cells Syst (Seoul). 2025 Jan 10;29(1):72-83. doi: 10.1080/19768354.2024.2449518. eCollection 2025. Anim Cells Syst (Seoul). 2025. PMID: 39807350 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Automated model refinement using perturbation-observation pairs.NPJ Syst Biol Appl. 2025 Jun 16;11(1):65. doi: 10.1038/s41540-025-00532-y. NPJ Syst Biol Appl. 2025. PMID: 40523884 Free PMC article.
-
A Model for the Gene Regulatory Network Along the Arabidopsis Fruit Medio-Lateral Axis: Rewiring the Pod Shatter Process.Plants (Basel). 2024 Oct 18;13(20):2927. doi: 10.3390/plants13202927. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39458874 Free PMC article.
-
Inferring gene regulatory networks using transcriptional profiles as dynamical attractors.PLoS Comput Biol. 2023 Aug 22;19(8):e1010991. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1010991. eCollection 2023 Aug. PLoS Comput Biol. 2023. PMID: 37607190 Free PMC article.
-
Boolean network sketches: a unifying framework for logical model inference.Bioinformatics. 2023 Apr 3;39(4):btad158. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btad158. Bioinformatics. 2023. PMID: 37004199 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akutsu T., Miyano S., Kuhara S. (1999). Identification of genetic networks from a small number of gene expression patterns under the Boolean network model, in Pacific Symposium on Biocomputing, Vol. 4 (Hawaii: ), 17–28. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

