Prognostic role of elevated mir-24-3p in breast cancer and its association with the metastatic process
- PMID: 29560116
- PMCID: PMC5849180
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.24403
Prognostic role of elevated mir-24-3p in breast cancer and its association with the metastatic process
Abstract
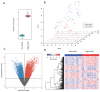
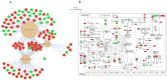
MicroRNAs have been shown to play important roles in breast cancer progression and can serve as biomarkers. To assess the prognostic role of a panel of miRNAs in breast cancer, we collected plasma prospectively at the time of initial diagnosis from 1,780 patients with stage I-III breast cancer prior to definitive treatment. We identified plasma from 115 patients who subsequently developed distant metastases and 115 patients without metastatic disease. Both groups were matched by: age at blood collection, year of blood collection, breast cancer subtype, and stage. The median follow up was 3.4 years (range, 1-9 years). We extracted RNA from plasma and analyzed the expression of 800 miRNAs using Nanostring technology. We then assessed the expression of miRNAs in primary and metastatic breast cancer samples from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA). We found that, miR-24-3p was upregulated in patients with metastases, both in plasma and in breast cancer tissues. Patients whose primary tumors expressed high levels of miR-24-3p had a significantly lower survival rate compared to patients with low mir-24-3p levels in the TCGA cohort (n=1,024). RNA-Seq data of the samples with the highest miR-24-3p expression versus those with the lowest miR-24-3p in the TCGA cohort identified a specific gene expression signature for those tumors with high miR-24-3p. Possible target genes for miR-24-3p were predicted based on gene expression and binding site, and their effects on cancer pathways were evaluated. Cancer, breast cancer and proteoglycans were the top three pathways affected by miR-24-3p overexpression.
Keywords: breast cancer; gene expression profiling.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Profiling of metastatic small intestine neuroendocrine tumors reveals characteristic miRNAs detectable in plasma.Oncotarget. 2017 Apr 7;8(33):54331-54344. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16908. eCollection 2017 Aug 15. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28903345 Free PMC article.
-
Differential expression profiles of microRNAs as potential biomarkers for the early diagnosis of lung cancer.Oncol Rep. 2017 Jun;37(6):3543-3553. doi: 10.3892/or.2017.5612. Epub 2017 Apr 28. Oncol Rep. 2017. PMID: 28498428
-
The highly expressed 5'isomiR of hsa-miR-140-3p contributes to the tumor-suppressive effects of miR-140 by reducing breast cancer proliferation and migration.BMC Genomics. 2016 Aug 8;17:566. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2869-x. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27502506 Free PMC article.
-
miR-410-3p suppresses breast cancer progression by targeting Snail.Oncol Rep. 2016 Jul;36(1):480-6. doi: 10.3892/or.2016.4828. Epub 2016 May 23. Oncol Rep. 2016. PMID: 27221455
-
Tumor tissue microRNA expression in association with triple-negative breast cancer outcomes.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2015 Jul;152(1):183-191. doi: 10.1007/s10549-015-3460-x. Epub 2015 Jun 11. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2015. PMID: 26062749 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Circulating miRNAs as Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers in Common Solid Tumors: Focus on Lung, Breast, Prostate Cancers, and Osteosarcoma.J Clin Med. 2019 Oct 11;8(10):1661. doi: 10.3390/jcm8101661. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 31614612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High Expression of microRNA-143 is Associated with Favorable Tumor Immune Microenvironment and Better Survival in Estrogen Receptor Positive Breast Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 1;21(9):3213. doi: 10.3390/ijms21093213. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32370060 Free PMC article.
-
Salivary exosomal microRNAs as biomarkers for head and neck cancer detection-a literature review.Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg. 2021 Jun 30;43(1):19. doi: 10.1186/s40902-021-00303-9. Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg. 2021. PMID: 34191144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cancer-associated fibroblast-derived exosomal microRNA-24-3p enhances colon cancer cell resistance to MTX by down-regulating CDX2/HEPH axis.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Apr;25(8):3699-3713. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15765. Epub 2021 Feb 23. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 33621425 Free PMC article.
-
The Intricate Interplay between Cancer Stem Cells and Oncogenic miRNAs in Breast Cancer Progression and Metastasis.Life (Basel). 2023 Jun 9;13(6):1361. doi: 10.3390/life13061361. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37374142 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Weigelt B, Peterse JL, van’t Veer LJ. Breast cancer metastasis: markers and models. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:591–602. - PubMed
-
- Friedrichs K, Kugler G, Franke F, Terpe HJ, Arlt J, Regidor PA, Gunthert U. CD44 isoforms in prognosis of breast cancer. Lancet. 1995;345:1237. - PubMed
-
- Kwa M, Makris A, Esteva FJ. Clinical utility of gene-expression signatures in early stage breast cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2017;14:595–610. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

