Relationship between cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (COMP) and rheumatoid arthritis severity
- PMID: 29560145
- PMCID: PMC5843419
- DOI: 10.19082/5940
Relationship between cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (COMP) and rheumatoid arthritis severity
Abstract
Background: Serum cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (COMP) is a non-collagen glycoprotein produced by the cartilage, synovium, tendon, and meniscus. Recent studies showed that COMP is a reliable factor for monitoring cartilage damage.
Objective: To determine the relationship between serum COMP concentration and the severity of rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Methods: This cross-sectional study lasted from 2013 to 2015 at the Rheumatology Clinic of Ghaem Hospital, Mashhad, Iran. The study population consisted of eligible patients who presented to our clinic during the study period. Four groups (150 subjects) were included as early RA (50 patients), late RA (50 patients), grades II and III OA (osteoarthritis) (25 cases, 17 grade II and 8 grade III joint destruction), and healthy controls (25 individuals). These were included consecutively. Serum COMP level was assessed by sandwich ELISA technique. In addition, ESR, hs-CRP, serum RF, and anti-CCP were assayed. X-rays of the knees (in OA) and hands (in RA) were examined for the degree of joint damage/erosion using the Short Erosion Scale (SES) in RA and Kellgren-Lawrence grading in OA. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) to compare mean COMP level among the groups and ROC (Receiver Operating Characteristic) analysis to determine the diagnostic accuracy of COMP in diagnosis of late RA were used by SPSS software (ver. 20.0).
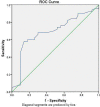
Results: Mean (±SD) serum COMP levels were 18 (±10.6) U/L in early RA, 19.3 (±9.6) U/L in late RA, 10.9 (±4.5) U/L in OA, and 4.2 (±3.8) in controls; p<0.001. Serum COMP level was higher in RA and OA groups when compared to control group. Mean (±SD) SES score was 13.5 (±7.5) in early RA and 16.4 (±9.7) in late RA (p=0.093). There was a significant positive correlation between COMP level and disease severity in early RA (r=0.677, p<0.001) as well as in late RA (r=0.753, p<0.001). Serum COMP level at a concentration of 15.25 U/L had a sensitivity of 68% and specificity of 70% to discriminate late RA from early RA (area under curve= 69% (95% CI: 58% to 79%; p=0.001).
Conclusion: COMP had positive significant correlation with early and late RA severity. This serum biomarker can be a useful and easy tool for monitoring of RA patients either at early or late stages of the disease.
Keywords: Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (COMP); Extracellular matrix proteins; Rheumatoid arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: There is no conflict of interest to be declared.
Figures
References
-
- Khanna R, Dlouhy BJ, Smith ZA, Lam SK, Koski TR, Dahdaleh NS. The impact of steroids, methotrexate, and biologics on clinical and radiographic outcomes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis undergoing fusions at the craniovertebral junction. J Craniovertebr Junction Spine. 2015;6(2):60–4. doi: 10.4103/0974-8237.156044. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous