The boron-boron triple bond? A thermodynamic and force field based interpretation of the N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC) stabilization procedure
- PMID: 29560205
- PMCID: PMC5811121
- DOI: 10.1039/c4sc02997f
The boron-boron triple bond? A thermodynamic and force field based interpretation of the N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC) stabilization procedure
Abstract
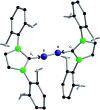
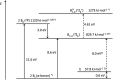
Recently, the NHC→B[triple bond, length as m-dash]B←NHC molecule 1 has been published in Science where it is described as a stabilized B2 molecule in its 1Σ excited state (B2*) (NHC = N-heterocyclic carbene C3N2H2(C6H3Pri 2-2,6)2). The bonding of 1 based on sophisticated calculations and the BB distances of the solid compound was discussed as the first example of a B2 triple bond in a stable molecule. Now we present an only experimentally based interpretation of 1 via detailed thermodynamic considerations, including its fragmentation to B2 molecules. Furthermore, from the vibrational spectrum force constants (f BB for the BB bond and f BC for the BC bond) were extracted, which are classical examples to indicate single, double and triple CC bonds in organic chemistry. The consequence of both properties of 1 (ΔE and f) generates a new interpretation which is in contrast to the triple bond donor-acceptor description visualized by arrows and which casts a critical light on the interpretation of any NHC "stabilized" molecule.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015.
Figures

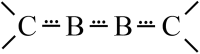
Similar articles
-
The boron-boron triple bond in NHC→B[triple bond, length as m-dash]B←NHC.Chem Sci. 2015 Jul 1;6(7):4089-4094. doi: 10.1039/c5sc01504a. Epub 2015 Jun 1. Chem Sci. 2015. PMID: 29218175 Free PMC article.
-
Stabilization of Boron-Boron Triple Bonds by Mesoionic Carbenes.ACS Omega. 2018 Oct 19;3(10):13720-13730. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.8b02305. eCollection 2018 Oct 31. ACS Omega. 2018. PMID: 31458073 Free PMC article.
-
Dehydrogenation of saturated CC and BN bonds at cationic N-heterocyclic carbene stabilized M(III) centers (M = Rh, Ir).J Am Chem Soc. 2010 Aug 4;132(30):10578-91. doi: 10.1021/ja1043787. J Am Chem Soc. 2010. PMID: 20662531
-
Silavinylidene stabilized by an N-heterocyclic carbene: a theoretically predicted stable molecule.Chemistry. 2014 Jul 21;20(30):9216-20. doi: 10.1002/chem.201403252. Epub 2014 Jun 4. Chemistry. 2014. PMID: 24899112
-
Application of N-heterocyclic carbene-Cu(I) complexes as catalysts in organic synthesis: a review.Beilstein J Org Chem. 2023 Sep 20;19:1408-1442. doi: 10.3762/bjoc.19.102. eCollection 2023. Beilstein J Org Chem. 2023. PMID: 37767335 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Boron-based octahedral dication experimentally detected: DFT surface confirms its availability.RSC Adv. 2023 Jun 28;13(28):19627-19637. doi: 10.1039/d3ra03665k. eCollection 2023 Jun 22. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 37388141 Free PMC article.
-
III-defined concepts in chemistry: rigid force constants vs. compliance constants as bond strength descriptors for the triple bond in diboryne.Chem Sci. 2015 Jul 1;6(7):4086-4088. doi: 10.1039/c5sc01322d. Epub 2015 May 4. Chem Sci. 2015. PMID: 29218174 Free PMC article.
-
The boron-boron triple bond in NHC→B[triple bond, length as m-dash]B←NHC.Chem Sci. 2015 Jul 1;6(7):4089-4094. doi: 10.1039/c5sc01504a. Epub 2015 Jun 1. Chem Sci. 2015. PMID: 29218175 Free PMC article.
-
Spying on the boron-boron triple bond using spin-spin coupling measured from 11B solid-state NMR spectroscopy.Chem Sci. 2015 Jun 1;6(6):3378-3382. doi: 10.1039/c5sc00644a. Epub 2015 Apr 1. Chem Sci. 2015. PMID: 29142694 Free PMC article.
-
How to Stabilize Carbenes in Enzyme Active Sites without Metal Ions.J Am Chem Soc. 2022 Nov 16;144(45):20739-20751. doi: 10.1021/jacs.2c08515. Epub 2022 Nov 3. J Am Chem Soc. 2022. PMID: 36326587 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dalton Discussion 11: The Renaissance of Main Group Elements; Dalton Trans. 2008, 33, 4321–4524.. - PubMed
-
- Ecker A., Weckert E., Schnöckel H. Nature. 1997;387:379.
-
- Tran N. T., Powell D. R., Dahl L. F. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2000;39:4121. - PubMed
-
- Jadzinsky P. D., Calero G., Ackerson C. J., Bushnell D. A., Kornberg R. D. Science. 2007;318:430. - PubMed
-
- Whetten R. L., Price R. C. Science. 2007;318:407. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

