The role of tumor microenvironment in resistance to anti-angiogenic therapy
- PMID: 29560266
- PMCID: PMC5854986
- DOI: 10.12688/f1000research.11771.1
The role of tumor microenvironment in resistance to anti-angiogenic therapy
Abstract
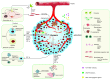
Anti-angiogenic therapy has been demonstrated to increase progression-free survival in patients with many different solid cancers. Unfortunately, the benefit in overall survival is modest and the rapid emergence of drug resistance is a significant clinical problem. Over the last decade, several mechanisms have been identified to decipher the emergence of resistance. There is a multitude of changes within the tumor microenvironment (TME) in response to anti-angiogenic therapy that offers new therapeutic opportunities. In this review, we compile results from contemporary studies related to adaptive changes in the TME in the development of resistance to anti-angiogenic therapy. These include preclinical models of emerging resistance, dynamic changes in hypoxia signaling and stromal cells during treatment, and novel strategies to overcome resistance by targeting the TME.
Keywords: MET signaling; anti-angiogenic therapy; drug resistance; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: RLC has received grant funding from Genentech, Merck, Janssen, Clovis, AZ, and Abbvie and serves on the scientific steering committee as an investigator for Tesaro, Clovis, AZ, and Abbvie. AKS serves on the advisory board for Kiyatec and has received research funding from M-Trap. The other authors declare that they have no competing interests.No competing interests were disclosed.No competing interests were disclosed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting the Tumor Microenvironment in Renal Cell Cancer Biology and Therapy.Front Oncol. 2019 Jun 14;9:490. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00490. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31259150 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adaptive Mechanisms of Tumor Therapy Resistance Driven by Tumor Microenvironment.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Mar 1;9:641469. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.641469. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33732706 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypoxic tumor microenvironment: Implications for cancer therapy.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2020 Jul;245(13):1073-1086. doi: 10.1177/1535370220934038. Epub 2020 Jun 27. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2020. PMID: 32594767 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Taking a Full Snapshot of Cancer Biology: Deciphering the Tumor Microenvironment for Effective Cancer Therapy in the Oncology Clinic.OMICS. 2020 Apr;24(4):175-179. doi: 10.1089/omi.2020.0019. Epub 2020 Mar 13. OMICS. 2020. PMID: 32176591 Review.
-
Tumor Microenvironment and Nitric Oxide: Concepts and Mechanisms.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1277:143-158. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-50224-9_10. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 33119871
Cited by
-
Evaluation of the impact of Roclaglamide on MDA-MB-231 human breast adenocarcinoma cells by cell culture and molecular approaches.Saudi Pharm J. 2025 Jul 8;33(4):22. doi: 10.1007/s44446-025-00023-5. Saudi Pharm J. 2025. PMID: 40627085 Free PMC article.
-
Reactive Oxygen Species Induce Endothelial Differentiation of Liver Cancer Stem-Like Sphere Cells through the Activation of Akt/IKK Signaling Pathway.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Oct 10;2020:1621687. doi: 10.1155/2020/1621687. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 33101583 Free PMC article.
-
Microphysiological model of renal cell carcinoma to inform anti-angiogenic therapy.Biomaterials. 2022 Apr;283:121454. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2022.121454. Epub 2022 Mar 11. Biomaterials. 2022. PMID: 35299086 Free PMC article.
-
Selective delivery of PLXDC1 small interfering RNA to endothelial cells for anti-angiogenesis tumor therapy using CD44-targeted chitosan nanoparticles for epithelial ovarian cancer.Drug Deliv. 2018 Nov;25(1):1394-1402. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2018.1480672. Drug Deliv. 2018. PMID: 29890852 Free PMC article.
-
CD63-mediated cloaking of VEGF in small extracellular vesicles contributes to anti-VEGF therapy resistance.Cell Rep. 2021 Aug 17;36(7):109549. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109549. Cell Rep. 2021. PMID: 34407412 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

