Vaccination route can significantly alter the innate lymphoid cell subsets: a feedback between IL-13 and IFN-γ
- PMID: 29560282
- PMCID: PMC5847557
- DOI: 10.1038/s41541-018-0048-6
Vaccination route can significantly alter the innate lymphoid cell subsets: a feedback between IL-13 and IFN-γ
Abstract
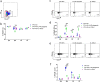
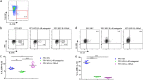
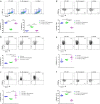
This study demonstrates that the fate of a vaccine is influenced by the cytokines produced by the innate lymphoid cells (ILC) recruited to the vaccination site, and it is vaccine route and adjuvant dependent. Intranasal virus vaccination induced ST2/IL-33R+ ILC2 in lung, while intramuscular vaccination induced exclusively IL-25R+ ILC2 in muscle. Interestingly, a larger proportion of IL-13+ ILC2s were detected in muscle following i.m. viral vector vaccination compared to lung post i.n. delivery. These observations revealed that ILC2 were the main source of IL-13 at the vaccination site (24 h post vaccination) responsible for inducing T cells of varying avidities. Moreover, recombinant fowlpox viral vector-based vaccines expressing adjuvants that transiently block IL-13 signalling at the vaccination site using different mechanisms (IL-4R antagonist or IL-13Rα2 adjuvants), revealed that the level of IL-13 present in the milieu also significantly influenced IFN-γ, IL-22 or IL-17A expression by ILC1/ILC3. Specifically, an early IL-13 and IFN-γ co-dependency at the ILC level may also be associated with shaping the downstream antibody responses, supporting the notion that differentially regulating IL-13 signalling via STAT6 or IL-13Rα2 pathways can modify ILC function and the resulting adaptive T- and B-cell immune outcomes reported previously. Moreover, unlike chronic inflammatory or experimentally induced conditions, viral vector vaccination induced uniquely different ILC profiles (i.e., expression of CD127 only on ILC2 not ILC1/ILC3; expression of IFN-γ in both NKP46+ and NKp46- ILCs). Collectively, our data highlight that tailoring a vaccine vector/adjuvant to modulate the ILC cytokine profile according to the target pathogen, may help design more efficacious vaccines in the future.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

