A Myth Still Needs to be Clarified: A Case Report of the Frank's Sign
- PMID: 29560293
- PMCID: PMC5856409
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.2080
A Myth Still Needs to be Clarified: A Case Report of the Frank's Sign
Abstract
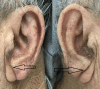
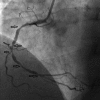
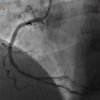
Despite advancements in diagnostic tools, physical signs such as xanthelasmata, arcus corneae, facial wrinkles, and gray hair are useful indicators of underlying diseases. The presence of bilateral diagonal earlobe creases (DELCs), also known as Frank's sign, correlates with a myriad of cardiovascular diseases such as coronary artery disease, cerebrovascular disease, and peripheral vascular disease. The use of Frank's sign as a bedside predictor of underlying coronary artery disease is controversial among clinicians. We report a case of a patient with bilateral DELCs found to have significant coronary artery disease during diagnostic coronary angiography for recurrent chest pain.
Keywords: bilateral diagonal ear lobe creases; cardiology; coronary heart disease; frank's sign.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Aural sign of coronary-artery disease. Frank ST. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/4718047 New Eng J Med. 1973;289:327–328. - PubMed
-
- Diagonal earlobe creases and prognosis in patients with suspected coronary artery disease. Elliott WJ, Powell LH. Am J Med. 1996;100:205–211. - PubMed
-
- Bilateral earlobe creases and coronary artery disease. Sharma A, Obiagwu C, Sikorskaya E. Cleve Clin J Med. 2016;83:786–787. - PubMed
-
- Bilateral earlobe creases and coronary artery disease. Qamar A, Ioannides KL, Khetarpal SA, Kiss D. Circulation. 2014;130:92–93. - PubMed
-
- Earlobe crease in patient with chest pain. Contou D, Lecronier M, Urbina T, de Prost N. Ann Emerg Med. 2017;69:664–672. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources