Don't forget the hip! Hip arthritis masquerading as knee pain
- PMID: 29560406
- PMCID: PMC5859208
- DOI: 10.1016/j.artd.2017.06.008
Don't forget the hip! Hip arthritis masquerading as knee pain
Abstract
Background: Hip osteoarthritis typically manifests with groin or thigh pain. Other atypical pain patterns, including knee pain, have been described. Except for 2 case reports, there is no literature on this subject.
Methods: From our institutional database, between 2011 and 2016, we identified 21 patients who were referred for treatment of knee pain but ultimately diagnosed with hip pathology as the cause of their pain. This group was evaluated for duration of symptoms prior to diagnosis, previous interventions, presence of walking aids, and symptom resolution after treatment of the hip pathology.
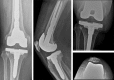
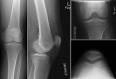
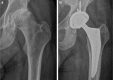
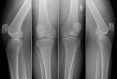
Results: Fifteen of the 21 patients were referred from musculoskeletal providers (12 from orthopaedic surgeons). Prior to diagnosis of the hip etiology, 16 patients were reduced to major assistive devices including wheelchairs. Twelve of 21 patients had undergone surgical knee interventions, including total knee arthroplasty, with minimal to no relief of their pain. Seventeen of 21 referred patients underwent total hip arthroplasty at our institution. Fourteen patients had complete resolution of knee pain after total hip arthroplasty.
Conclusions: Although knee pain referred from hip disease may be considered a basic and common knowledge, it continues to be an overlooked phenomenon. Most of the cases were misdiagnosed by musculoskeletal providers including orthopaedic surgeons and this highlights the need for continued education and awareness of this clinical scenario.
Keywords: Delay in diagnosis; Hip pain; Knee pain; Referred pain; Unnecessary surgery.
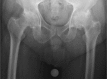
Figures


Similar articles
-
Outcome of hip and knee arthroplasty in persons aged 80 years and older.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1997 Dec;(345):67-78. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1997. PMID: 9418623
-
Postoperative pain and patient satisfaction are not influenced by daytime and duration of knee and hip arthroplasty: a prospective cohort study.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2017 Oct;137(10):1343-1348. doi: 10.1007/s00402-017-2769-9. Epub 2017 Aug 3. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2017. PMID: 28776090
-
Bilateral Total Hip and Knee Arthroplasties: Average 10-Year Follow-Up.J Arthroplasty. 2017 Nov;32(11):3328-3332. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2017.05.029. Epub 2017 May 22. J Arthroplasty. 2017. PMID: 28602534
-
Determining who should be referred for total hip and knee replacements.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2013 Jun;9(6):351-7. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2013.27. Epub 2013 Mar 12. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2013. PMID: 23478495 Review.
-
Total Hip and Knee arthroplasty in a patient with osteopetrosis: a case report and review of the literature.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015 Sep 21;16:259. doi: 10.1186/s12891-015-0716-x. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015. PMID: 26391128 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic value of multiple projection angle X-ray and CT 3D reconstruction for long-term unreduced posterior hip dislocation.Front Surg. 2025 May 8;12:1512955. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2025.1512955. eCollection 2025. Front Surg. 2025. PMID: 40405902 Free PMC article.
-
Musculoskeletal mimics of lumbosacral radiculopathy.Muscle Nerve. 2025 May;71(5):816-832. doi: 10.1002/mus.28106. Epub 2024 May 10. Muscle Nerve. 2025. PMID: 38726566 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Pediatric Hip Physical Exam.Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2025 Apr;18(4):103-114. doi: 10.1007/s12178-025-09945-y. Epub 2025 Jan 25. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2025. PMID: 39862342 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sacks J.J., Luo Y.H., Helmick C.G. Prevalence of specific types of arthritis and other rheumatic conditions in the ambulatory health care system in the United States, 2001–2005. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2010;62(4):460. - PubMed
-
- Arthritis and related conditions, chapter 4. http://www.boneandjointburden.org/2013-report/iv-arthritis/iv [accessed 27.01.17]
-
- Jordan J.M., Helmick C.G., Renner J.B. Prevalence of knee symptoms and radiographic and symptomatic knee osteoarthritis in African Americans and Caucasians: the Johnston County Osteoarthritis Project. J Rheumatol. 2007;34(1):172. - PubMed
-
- Hasan M., Shuckett R. Clinical features and pathogenetic mechanisms of osteoarthritis of the hip and knee. BCMJ. 2010;52(8):393.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

