Protective effect of compound Danshen (Salvia miltiorrhiza) dripping pills alone and in combination with carbamazepine on kainic acid-induced temporal lobe epilepsy and cognitive impairment in rats
- PMID: 29560767
- PMCID: PMC6130614
- DOI: 10.1080/13880209.2018.1432665
Protective effect of compound Danshen (Salvia miltiorrhiza) dripping pills alone and in combination with carbamazepine on kainic acid-induced temporal lobe epilepsy and cognitive impairment in rats
Abstract
Context: Temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE) is resistant to antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) and is associated with cognitive impairment. The modern Chinese medicine, compound Danshen dripping pills (CDDP), is clinically effective in treating epilepsy and improving cognitive impairment.
Objective: This study evaluated the protective effects of CDDP alone and in combination with carbamazepine (CBZ) on kainic acid-induced TLE and cognitive impairment in rats.
Materials and methods: Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly divided into five groups: control (sham operated), model, CDDP, CBZ and combined. A TLE model was then created via bilateral intrahippocampal injection of 0.35 μg kainic acid (KA). Rats received CDDP (85 mg/kg), CBZ (100 mg/kg) or combined (85 mg/kg CDDP +100 mg/kg CBZ) via intragastric administration for 90 d, respectively. Seizure intensity, apoptosis and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) were measured. Furthermore, the improvement in cognitive impairment and hippocampal neuronal damage was evaluated.
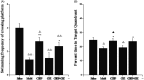
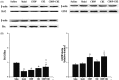
Results: CDDP combined with CBZ significantly decreased seizure severity and frequency (p < 0.05) and ameliorated cognitive impairment (p < 0.05). The model group showed a significant reduction of neurons and Bcl-2/Bax expression in the hippocampus CA3 area (p < 0.01), the combined groups significantly reversed these change (p < 0.01). GDNF expression in the combined groups showed a clear increase over the model group (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: These findings support the use of CDDP as an adjuvant drug for the treatment of TLE and cognitive deficit. Its mechanism might be related to an anti-apoptosis effect and up-regulation of GDNF.
Keywords: Intractable epilepsy; anti-apoptosis; antiepileptic drugs; glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor; hippocampal CA3 area; traditional Chinese medicine.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Neuronal protective effect of Songling Xuemaikang capsules alone and in combination with carbamazepine on epilepsy in kainic acid-kindled rats.Pharm Biol. 2019 Dec;57(1):22-28. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2018.1563619. Pharm Biol. 2019. PMID: 30724642 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective Effect of Electric Conduction Treatment on Hippocampus Cell Apoptosis in KA Induced Acute Temporal Lobe Epileptic Rats.Brain Stimul. 2016 Nov-Dec;9(6):933-939. doi: 10.1016/j.brs.2016.07.011. Epub 2016 Aug 2. Brain Stimul. 2016. PMID: 27553886
-
Bupropion attenuates kainic acid-induced seizures and neuronal cell death in rat hippocampus.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2013 Aug 1;45:207-14. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2013.05.016. Epub 2013 Jun 11. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2013. PMID: 23770308
-
Compound Danshen Dripping Pill inhibits high altitude-induced hypoxic damage by suppressing oxidative stress and inflammatory responses.Pharm Biol. 2021 Dec;59(1):1585-1593. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2021.1998139. Pharm Biol. 2021. PMID: 34808069 Free PMC article.
-
Potential causes of cognitive alterations in temporal lobe epilepsy.Behav Brain Res. 2020 Jan 27;378:112310. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2019.112310. Epub 2019 Oct 16. Behav Brain Res. 2020. PMID: 31629002 Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy and safety of Chinese herbal medicine in post-stroke epilepsy: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Nov 21;14:1286093. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1286093. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 38074155 Free PMC article.
-
Asiatic Acid Prevents Cognitive Deficits by Inhibiting Calpain Activation and Preserving Synaptic and Mitochondrial Function in Rats with Kainic Acid-Induced Seizure.Biomedicines. 2021 Mar 10;9(3):284. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9030284. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 33802221 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of the mechanism of tanshinone IIA to improve cognitive function via synaptic plasticity in epileptic rats.Pharm Biol. 2023 Dec;61(1):100-110. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2022.2157843. Pharm Biol. 2023. PMID: 36548216 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Mixtures of Emerging Pollutants and Drugs on Modulation of Biomarkers Related to Toxicity, Oxidative Stress, and Cancer.Metabolites. 2024 Oct 17;14(10):559. doi: 10.3390/metabo14100559. Metabolites. 2024. PMID: 39452940 Free PMC article.
-
A narrative review on traditional Chinese medicine prescriptions and bioactive components in epilepsy treatment.Ann Transl Med. 2023 Jan 31;11(2):129. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-3306. Epub 2022 Dec 13. Ann Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 36819494 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Airaksinen MS, Saarma M.. 2002. The GDNF family: signalling, biological functions and therapeutic value. Nat Rev Neurosci. 3:383–394. - PubMed
-
- Bahadir A, Demir S, Orallar H, Beyazcicek E, Oner F.. 2015. Effects of an extract of Salvia miltiorrhiza on a penicillin-induced epilepsy model in rats. Neurophysiology. 47:1–7.
-
- Bell BD, Giovagnoli AR.. 2007. Recent innovative studies of memory in temporal lobe epilepsy. Neuropsychol Rev. 17:455–476. - PubMed
-
- Bell GS, Sander JW.. 2001. The epidemiology of epilepsy: the size of the problem. Seizure. 10:306–316. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y, Ginis I, Hallenbeck JM.. 2001. The protective effect of ceramide in immature rat brain hypoxia-isch involves up-regulation of Bcl-2 and reduction of TUNEL-positive cells. Neurol Res. 32:82–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
