Rivaroxaban versus nadroparin for preventing deep venous thrombosis after total hip arthroplasty following femoral neck fractures: A retrospective comparative study
- PMID: 29560772
- PMCID: PMC5991221
- DOI: 10.1177/0300060518762281
Rivaroxaban versus nadroparin for preventing deep venous thrombosis after total hip arthroplasty following femoral neck fractures: A retrospective comparative study
Abstract
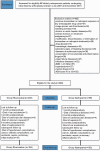
Objective This study was performed to evaluate the efficacy of rivaroxaban versus nadroparin for preventing deep venous thrombosis (DVT) in elderly patients with osteoporosis undergoing initial total hip arthroplasty (THA) for femoral neck fractures. Methods Prospectively maintained databases were reviewed to retrospectively compare elderly patients with osteoporosis who underwent initial THA for femoral neck fractures from 2007 to 2015. The patients received peroral rivaroxaban at 10 mg/day for 2 weeks or subcutaneous injections of nadroparin at 0.3 mL/day for 2 weeks until the primary analysis cut-off date. The time to first on-study DVT was the primary endpoint. Results In total, 399 patients were included (rivaroxaban group: n=200; mean age, 70.20 ± 9.16 years and nadroparin group: n = 199; mean age, 69.90 ± 8.87 years), with a mean 3-year follow-up. The time to first on-study DVT was significantly longer in the rivaroxaban than nadroparin group (12 and 5 days, respectively). The incidence of DVT within the 2-week follow-up was significantly higher in the nadroparin than rivaroxaban group (6.8% and 19.7%, respectively), but this difference was no longer present at the final follow-up. Conclusion Rivaroxaban was associated with a significant reduction in the occurrence of first on-study DVT compared with nadroparin.
Keywords: Rivaroxaban; deep venous thrombosis; femoral neck fracture; nadroparin; osteoporosis; total hip arthroplasty.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of rivaroxaban on preventing deep vein thrombosis in aged diabetics with femoral neck fractures after hip replacement.Biosci Rep. 2017 Jun 21;37(3):BSR20170289. doi: 10.1042/BSR20170289. Print 2017 Jun 30. Biosci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28442600 Free PMC article.
-
Postoperative plasma D-dimer value for predicting deep venous thrombosis following hip arthroplasty with nadroparin prophylaxis.Hip Int. 2013 Jul-Aug;23(4):411-6. doi: 10.5301/hipint.5000039. Epub 2013 Aug 25. Hip Int. 2013. PMID: 24027038
-
Comparison of efficacy of nadroparin and fondaparinux sodium for prevention of deep vein thromboembolism in lower extremities after total hip arthroplasty and total knee arthroplasty: a retrospective study of 592 patients.BMC Surg. 2024 May 18;24(1):162. doi: 10.1186/s12893-024-02440-0. BMC Surg. 2024. PMID: 38762739 Free PMC article.
-
Chinese Herbal Medicines for Promoting Blood Circulation and Removing Blood Stasis for Preventing Deep Venous Thrombosis after Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2021;24(7):893-907. doi: 10.2174/1386207323666200901103732. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2021. PMID: 32875979
-
Deep Vein Thrombosis in a Young, Healthy Baseball Catcher: A Case Report and Review of the Literature.J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2019 May;41(4):321-323. doi: 10.1097/MPH.0000000000001113. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2019. PMID: 29401105 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of 3 different anticoagulants on hidden blood loss during total hip arthroplasty after tranexamic acid.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Sep 4;99(36):e22028. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000022028. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32899057 Free PMC article.
-
[Comparison of hemostatic effect and safety in primary unilateral total hip arthroplasty receiving different anticoagulants after anti-fibrinolysis with tranexamic acid].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020 Dec 15;34(12):1561-1567. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.202006007. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 33319536 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Predictive value of miR-374a-5p of peripheral blood mononuclear cells in deep venous thrombosis for elderly patients after total hip arthroplasty.Am J Transl Res. 2021 Sep 15;13(9):10670-10675. eCollection 2021. Am J Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 34650741 Free PMC article.
-
Rivaroxaban vs. enoxaparin for preventing venous thromboembolism after hip fracture operations: a retrospective cohort study.Front Surg. 2025 May 9;12:1483611. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2025.1483611. eCollection 2025. Front Surg. 2025. PMID: 40416725 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zeng X, Zhan K, Zhang L, et al. Conversion to total hip arthroplasty after failed proximal femoral nail antirotations or dynamic hip screw fixations for stable intertrochanteric femur fractures: a retrospective study with a minimum follow-up of 3 years. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2017; 18: 38. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zou Y, Tian SQ, Wang YH, et al. Administering aspirin, rivaroxaban and low-molecular-weight heparin to prevent deep venous thrombosis after total knee arthroplasty. Blood Coagul Fibrin 2014; 25: 660–664. - PubMed
-
- Lazo-Langner A, Fleet JL, McArthur E, et al. Rivaroxaban vs. low molecular weight heparin for the prevention of venous thromboembolism after hip or knee arthroplasty: a cohort study. J Thromb Haemost 2014; 12: 1626–1635. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

