Moving epidemic method (MEM) applied to virology data as a novel real time tool to predict peak in seasonal influenza healthcare utilisation. The Scottish experience of the 2017/18 season to date
- PMID: 29560854
- PMCID: PMC5861591
- DOI: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2018.23.11.18-00079
Moving epidemic method (MEM) applied to virology data as a novel real time tool to predict peak in seasonal influenza healthcare utilisation. The Scottish experience of the 2017/18 season to date
Abstract
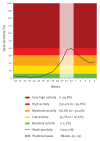
Scotland observed an unusual influenza A(H3N2)-dominated 2017/18 influenza season with healthcare services under significant pressure. We report the application of the moving epidemic method (MEM) to virology data as a tool to predict the influenza peak activity period and peak week of swab positivity in the current season. This novel MEM application has been successful locally and is believed to be of potential use to other countries for healthcare planning and building wider community resilience.
Keywords: Scotland; epidemiology; influenza; influenza virus; laboratory; laboratory surveillance; modelling; policy; sentinel surveillance; statistics; viral infections.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- BBC News Scotland. Health expert warns of flu impact on operations. January 12th 2018. [Accessed 07 Feb 2018]. Available from: http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/uk-scotland-42661886
-
- Pebody R, Warburton F, Ellis J, Andrews N, Potts A, Cottrell S, et al. Effectiveness of seasonal influenza vaccine for adults and children in preventing laboratory-confirmed influenza in primary care in the United Kingdom: 2015/16 end-of-season results. Euro Surveill. 2016;21(38):30348. . Available from: https://doi.org/10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2016.21.38.30348 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2016.21.38.30348 - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Health Protection Scotland. The Electronic Communication of Surveillance in Scotland (ECOSS). Available from: http://www.hps.scot.nhs.uk/surveillance/SystemsDetail.aspx?id=248 date a...
-
- Green HK, Charlett A, Moran-Gilad J, Fleming D, Durnall H, Thomas DR, et al. Harmonizing influenza primary-care surveillance in the United Kingdom: piloting two methods to assess the timing and intensity of the seasonal epidemic across several general practice-based surveillance schemes. Epidemiol Infect. 2015;143(1):1-12. 10.1017/S0950268814001757 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
