Measurement of Serum and Hepatic Eicosanoids by Liquid Chromatography Tandem-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) in a Mouse Model of Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) with Delivery of c-Met and Activated β-Catenin by Hepatocyte Hydrodynamic Injection
- PMID: 29560932
- PMCID: PMC5877205
- DOI: 10.12659/msm.908931
Measurement of Serum and Hepatic Eicosanoids by Liquid Chromatography Tandem-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) in a Mouse Model of Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) with Delivery of c-Met and Activated β-Catenin by Hepatocyte Hydrodynamic Injection
Abstract
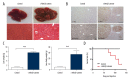
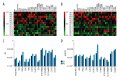
BACKGROUND Most forms of cancer, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), are associated with varying degrees of chronic inflammation. The association between the expression of eicosanoids, which are bioactive lipid mediators of inflammation, and HCC remains unknown. The aim of this study was to measure serum and hepatic eicosanoids in a mouse model of HCC with the delivery of c-Met and activated b-catenin by hepatocyte hydrodynamic injection. MATERIAL AND METHODS The HCC mouse model, and normal control mice, were used in this study with co-delivery of human c-Met combined with activated β-catenin into hepatocytes through hydrodynamic injection. Liquid chromatography tandem-mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) analysis was used to measure serum and hepatic eicosanoid levels. RESULTS The combined activation of c-Met and β-catenin was induced in the HCC mouse model. LC-MS/MS showed that a total of 13 eicosanoids in serum and 12 eicosanoids in liver tissue were significantly increased in the HCC mice, when compared with control mice. CONCLUSIONS In a mouse model of HCC, co-activation of the c-Met and β-catenin signaling pathway resulted in increased levels of serum and hepatic eicosanoids.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Notch activity characterizes a common hepatocellular carcinoma subtype with unique molecular and clinicopathologic features.J Hepatol. 2021 Mar;74(3):613-626. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.09.032. Epub 2020 Oct 8. J Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 33038431 Free PMC article.
-
Shp2 deletion in hepatocytes suppresses hepatocarcinogenesis driven by oncogenic β-Catenin, PIK3CA and MET.J Hepatol. 2018 Jul;69(1):79-88. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.02.014. Epub 2018 Mar 2. J Hepatol. 2018. PMID: 29505847 Free PMC article.
-
TBX3 functions as a tumor suppressor downstream of activated CTNNB1 mutants during hepatocarcinogenesis.J Hepatol. 2021 Jul;75(1):120-131. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.01.044. Epub 2021 Feb 10. J Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 33577921 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of eicosanoids by LC-MS/MS and GC-MS/MS: a historical retrospect and a discussion.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2014 Aug 1;964:79-88. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2014.03.017. Epub 2014 Mar 21. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 24742369 Review.
-
Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for the analysis of eicosanoids and related lipids in human biological matrices: a review.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2014 Aug 1;964:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2014.01.046. Epub 2014 Feb 8. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 24583205 Review.
Cited by
-
Eicosanoids and other oxylipins in liver injury, inflammation and liver cancer development.Front Physiol. 2023 Feb 2;14:1098467. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1098467. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36818443 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantification of eicosanoids and their metabolites in biological matrices: a review.Bioanalysis. 2018 Dec;10(24):2027-2046. doi: 10.4155/bio-2018-0173. Epub 2018 Nov 6. Bioanalysis. 2018. PMID: 30412686 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolomics and Lipidomics Screening Reveal Reprogrammed Signaling Pathways toward Cancer Development in Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 22;24(1):210. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010210. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36613653 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous Quantification of Serum Lipids and Their Association with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus-Positive Hepatocellular Cancer.Metabolites. 2023 Jan 6;13(1):90. doi: 10.3390/metabo13010090. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 36677015 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the eicosanoid pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma.Am J Cancer Res. 2021 Jun 15;11(6):2456-2476. eCollection 2021. Am J Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34249410 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Clark T, Maximin S, Meier J, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma: Review of epidemiology, screening, imaging diagnosis, response assessment, and treatment. Curr Problems Diagn Radiol. 2015;44:479–86. - PubMed
-
- Umeda S, Kanda M, Kodera Y. Emerging evidence of molecular biomarkers in hepatocellular carcinoma. Histol Histopathol. 2017 [Epub ahead of print] - PubMed
-
- Klingenberg M, Matsuda A, Diederichs S, et al. Non-coding RNA in hepatocellular carcinoma: Mechanisms, biomarkers and therapeutic targets. J Hepatol. 2017;67:603–18. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

