Measurement of Serum and Hepatic Eicosanoids by Liquid Chromatography Tandem-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) in a Mouse Model of Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) with Delivery of c-Met and Activated β-Catenin by Hepatocyte Hydrodynamic Injection
- PMID: 29560932
- PMCID: PMC5877205
- DOI: 10.12659/msm.908931
Measurement of Serum and Hepatic Eicosanoids by Liquid Chromatography Tandem-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) in a Mouse Model of Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) with Delivery of c-Met and Activated β-Catenin by Hepatocyte Hydrodynamic Injection
Abstract
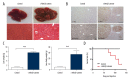
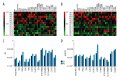
BACKGROUND Most forms of cancer, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), are associated with varying degrees of chronic inflammation. The association between the expression of eicosanoids, which are bioactive lipid mediators of inflammation, and HCC remains unknown. The aim of this study was to measure serum and hepatic eicosanoids in a mouse model of HCC with the delivery of c-Met and activated b-catenin by hepatocyte hydrodynamic injection. MATERIAL AND METHODS The HCC mouse model, and normal control mice, were used in this study with co-delivery of human c-Met combined with activated β-catenin into hepatocytes through hydrodynamic injection. Liquid chromatography tandem-mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) analysis was used to measure serum and hepatic eicosanoid levels. RESULTS The combined activation of c-Met and β-catenin was induced in the HCC mouse model. LC-MS/MS showed that a total of 13 eicosanoids in serum and 12 eicosanoids in liver tissue were significantly increased in the HCC mice, when compared with control mice. CONCLUSIONS In a mouse model of HCC, co-activation of the c-Met and β-catenin signaling pathway resulted in increased levels of serum and hepatic eicosanoids.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


References
-
- Clark T, Maximin S, Meier J, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma: Review of epidemiology, screening, imaging diagnosis, response assessment, and treatment. Curr Problems Diagn Radiol. 2015;44:479–86. - PubMed
-
- Umeda S, Kanda M, Kodera Y. Emerging evidence of molecular biomarkers in hepatocellular carcinoma. Histol Histopathol. 2017 [Epub ahead of print] - PubMed
-
- Klingenberg M, Matsuda A, Diederichs S, et al. Non-coding RNA in hepatocellular carcinoma: Mechanisms, biomarkers and therapeutic targets. J Hepatol. 2017;67:603–18. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

