Glucose transporter 2 mediates the hypoglycemia-induced increase in cerebral blood flow
- PMID: 29561214
- PMCID: PMC6727137
- DOI: 10.1177/0271678X18766743
Glucose transporter 2 mediates the hypoglycemia-induced increase in cerebral blood flow
Abstract
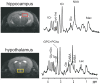
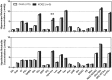
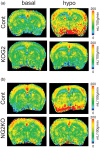
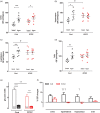
Glucose transporter 2 (Glut2)-positive cells are sparsely distributed in brain and play an important role in the stimulation of glucagon secretion in response to hypoglycemia. We aimed to determine if Glut2-positive cells can influence another response to hypoglycemia, i.e. increased cerebral blood flow (CBF). CBF of adult male mice devoid of Glut2, either globally (ripglut1:glut2-/-) or in the nervous system only (NG2KO), and their respective controls were studied under basal glycemia and insulin-induced hypoglycemia using quantitative perfusion magnetic resonance imaging at 9.4 T. The effect on CBF of optogenetic activation of hypoglycemia responsive Glut2-positive neurons of the paraventricular thalamic area was measured in mice expressing channelrhodopsin2 under the control of the Glut2 promoter. We found that in both ripglut1:glut2-/- mice and NG2KO mice, CBF in basal conditions was higher than in their respective controls and not further activated by hypoglycemia, as measured in the hippocampus, hypothalamus and whole brain. Conversely, optogenetic activation of Glut2-positive cells in the paraventricular thalamic nucleus induced a local increase in CBF similar to that induced by hypoglycemia. Thus, Glut2 expression in the nervous system is required for the control of CBF in response to changes in blood glucose concentrations.
Keywords: Glut2; cerebral blood flow; glut2 brain cells; hypoglycemia; optogenetic.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Regulation of glucagon secretion by glucose transporter type 2 (glut2) and astrocyte-dependent glucose sensors.J Clin Invest. 2005 Dec;115(12):3545-53. doi: 10.1172/JCI26309. J Clin Invest. 2005. PMID: 16322792 Free PMC article.
-
Glucose sensing by the hepatoportal sensor is GLUT2-dependent: in vivo analysis in GLUT2-null mice.Diabetes. 2000 Oct;49(10):1643-8. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.49.10.1643. Diabetes. 2000. PMID: 11016447
-
Desperately seeking sugar: glial cells as hypoglycemia sensors.J Clin Invest. 2005 Dec;115(12):3403-5. doi: 10.1172/JCI27208. J Clin Invest. 2005. PMID: 16322788 Free PMC article.
-
GLUT2, glucose sensing and glucose homeostasis.Diabetologia. 2015 Feb;58(2):221-32. doi: 10.1007/s00125-014-3451-1. Epub 2014 Nov 25. Diabetologia. 2015. PMID: 25421524 Review.
-
Brain glucose sensing and neural regulation of insulin and glucagon secretion.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2011 Oct;13 Suppl 1:82-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-1326.2011.01453.x. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2011. PMID: 21824260 Review.
Cited by
-
Hypoglycemia, Vascular Disease and Cognitive Dysfunction in Diabetes: Insights from Text Mining-Based Reconstruction and Bioinformatics Analysis of the Gene Networks.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 17;22(22):12419. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212419. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830301 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropeptides Modulate Feeding via the Dopamine Reward Pathway.Neurochem Res. 2023 Sep;48(9):2622-2643. doi: 10.1007/s11064-023-03954-4. Epub 2023 May 26. Neurochem Res. 2023. PMID: 37233918 Review.
-
Dietary Bioactive Ingredients Modulating the cAMP Signaling in Diabetes Treatment.Nutrients. 2021 Aug 30;13(9):3038. doi: 10.3390/nu13093038. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34578916 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in understanding hypothalamic control of defensive responses to hypoglycaemia.Curr Opin Endocr Metab Res. 2022 Jun;24:100353. doi: 10.1016/j.coemr.2022.100353. Curr Opin Endocr Metab Res. 2022. PMID: 39183767 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bitter taste cells in the ventricular walls of the murine brain regulate glucose homeostasis.Nat Commun. 2023 Mar 22;14(1):1588. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-37099-3. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 36949050 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Belanger M, Allaman I, Magistretti PJ. Brain energy metabolism: focus on astrocyte-neuron metabolic cooperation. Cell Metab 2011; 14: 724–738. - PubMed
-
- Bryan RM, Jr, Pelligrino DA. Cerebral blood flow during chronic hypoglycemia in the rat. Brain Res 1988; 475: 397–400. - PubMed
-
- Thomas M, Sherwin RS, Murphy J, et al. Importance of cerebral blood flow to the recognition of and physiological responses to hypoglycemia. Diabetes 1997; 46: 829–833. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

