The effect of corticosteroid versus platelet-rich plasma injection therapies for the management of lateral epicondylitis: A systematic review
- PMID: 29561260
- PMCID: PMC5861901
- DOI: 10.1051/sicotj/2017062
The effect of corticosteroid versus platelet-rich plasma injection therapies for the management of lateral epicondylitis: A systematic review
Abstract
Introduction: Lateral epicondylitis is a common musculoskeletal disorder of the upper limb. Corticosteroid injection has been widely used as a major mode of treatment. However, better understanding of the pathophysiology of the disease led to a major change in treating the disease, with new options including platelet-rich plasma (PRP) are currently used. Objectives/research aim: To systematically evaluate the effect of corticosteroid versus PRP injections for the treatment of LE.
Hypothesis: PRP injections provide longer-term therapeutic effect and less rate of complications compared to corticosteroid injection.
Level of evidence: Level 2 evidence (4 included studies are of level 1 evidence, 1 study of level 2 evidence).
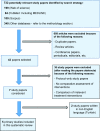
Design: Systematic Review (according to PRISMA guidelines).
Methods: Eleven databases used to search for relevant primary studies comparing the effects of corticosteroid and PRP injections for the treatment of LE. Quality appraisal of studies performed using Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0, CASP Randomised Controlled Trial Checklist, and SIGN Methodology Checklist 2.
Results: 732 papers were identified. Five randomised controlled trials (250 Patients) met the inclusion criteria.
Clinical findings: Corticosteroid injections provided rapid symptomatic improvement with maximum effect at 6/8/8 weeks before symptoms recurrence, whereas PRP showed slower ongoing improvements up to 24/52/104 weeks(3 studies). Corticosteroid showed more rapid symptomatic improvement of symptoms compared to PRP up to the study end-point of 3 months(1 study). Comparable therapeutic effects of corticosteroid and PRP were observed at 6 weeks(1 study). Ultrasonographic Findings: (1) Doppler activity decreased more significantly in patients who received corticosteroid compared to PRP. (2) Reduced tendon thickness and more patients with cortical erosion noted in corticosteroid group whereas increased tendon thickness and less number of patients with common extensor tendon tears noted in PRP group. (3) Fewer patients reported Probe-induced tenderness and oedema in the common extensor tendon in both corticosteroid and PRP groups (2 studies).
Conclusion: Corticosteroid injections provide rapid therapeutic effect in the short-term with recurrence of symptoms afterwards, compared to the relatively slower but longer-term effect of platelet-rich plasma.
© The Authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2018.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Platelet-rich plasma versus corticosteroid injection for recalcitrant lateral epicondylitis: clinical and ultrasonographic evaluation.J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2015 Apr;23(1):1-5. doi: 10.1177/230949901502300101. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2015. PMID: 25920633 Clinical Trial.
-
Platelet-Rich Plasma versus Corticosteroid Injection for the Treatment of Lateral Epicondylitis: A Systematic Review of Systematic Reviews.Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2021 Jun 1;16(3):597-605. doi: 10.26603/001c.24148. Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2021. PMID: 34123513 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of lateral epicondylitis with platelet-rich plasma, glucocorticoid, or saline: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.Am J Sports Med. 2013 Mar;41(3):625-35. doi: 10.1177/0363546512472975. Epub 2013 Jan 17. Am J Sports Med. 2013. PMID: 23328738 Clinical Trial.
-
Treatment of Lateral Epicondylitis With Autologous Blood, Platelet-Rich Plasma, or Corticosteroid Injections: A Systematic Review of Overlapping Meta-analyses.Orthop J Sports Med. 2019 Mar 14;7(3):2325967119831052. doi: 10.1177/2325967119831052. eCollection 2019 Mar. Orthop J Sports Med. 2019. PMID: 30899764 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Platelet-Rich Plasma Versus Corticosteroid Injection for Lumbar Spondylosis and Sacroiliac Arthropathy: A Systematic Review of Comparative Studies.Cureus. 2021 Mar 23;13(3):e14062. doi: 10.7759/cureus.14062. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 33898145 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Percutaneous ultrasound-guided ulnar nerve release technique compared to open technique: A cadaveric study.SICOT J. 2022;8:40. doi: 10.1051/sicotj/2022041. Epub 2022 Sep 26. SICOT J. 2022. PMID: 36155647 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic lateral epicondylitis: challenges and solutions.Open Access J Sports Med. 2018 Oct 30;9:243-251. doi: 10.2147/OAJSM.S160974. eCollection 2018. Open Access J Sports Med. 2018. PMID: 30464656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of the Clinical Results of Platelet-Rich Plasma, Steroid and Autologous Blood Injections in the Treatment of Chronic Lateral Epicondylitis.Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Mar 6;11(5):767. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11050767. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36900772 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Platelet-Rich Plasma Therapy for Knee Osteoarthritis: An In-Depth Analysis.J Funct Biomater. 2024 Aug 9;15(8):221. doi: 10.3390/jfb15080221. J Funct Biomater. 2024. PMID: 39194659 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of platelet-rich plasma versus steroid injection in plantar fasciitis: a randomized clinical trial.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023 Mar 7;24(1):172. doi: 10.1186/s12891-023-06277-1. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023. PMID: 36882804 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Shiri R, Viikari-Juntura E. (2011) Lateral and medial epicondylitis: role of occupational factors. Best Pr Res Clin Rheumatol 25(1), 43–57. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous