Preoperative platelet-albumin-bilirubin grades predict the prognosis of patients with hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma after liver resection: A retrospective study
- PMID: 29561452
- PMCID: PMC5895341
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000010226
Preoperative platelet-albumin-bilirubin grades predict the prognosis of patients with hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma after liver resection: A retrospective study
Abstract
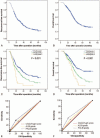
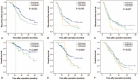
Minimal information is available concerning platelet-albumin-bilirubin (PALBI) grades in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) following liver resection. This study aimed to investigate the predictive ability of PALBI grades in patients with a Child-Pugh class A score and hepatitis B virus-related (HBV-related) HCC after liver resection.The data of patients with HBV-related HCC who underwent liver resection from 2010 to 2017 at our center were reviewed (n = 785). Cox regression was used to determine factors independently associated with postoperative recurrence and mortality. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) was used to estimate the predictive accuracy of different tools.During the follow-up period, 505 (64.3%) patients experienced recurrence, and 374 (47.6%) patients died. Multivariate analysis revealed that the tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) stage (HR = 1.591, 95%CI = 1.414-1.789, P < .001), PALBI grade (HR = 1.326, 95%CI = 1.139-1.544, P < .001), a high AFP level (HR = 1.382, 95%CI = 1.158-1.649, P < .001) and transfusion (HR = 1.364, 95%CI = 1.087-1.712, P = 0.007) were independently associated with recurrence. Additionally, microvascular invasion (HR = 1.674, 95%CI = 1.292-2.169, P < .001), beyond the Milan criteria (HR = 0.477, 95%CI = 0.346-0.657, P < .001), PALBI grade (HR = 1.356, 95%CI = 1.151-1.598, P < .001), a high AFP level (HR = 1.542, 95%CI = 1.252-1.900, P < .001), and transfusion (HR = 1.548, 95%CI = 1.199-1.999, P = 0.001) adversely impacted the overall survival. The AUCs of the PALBI grades for postoperative recurrence and mortality were significantly higher than the albumin-bilirubin grade and Child-Pugh score. The prognostic significance of the PALBI grade for postoperative recurrence and mortality was maintained when stratified by the TNM stage.The preoperative PALBI grade is a surrogate marker for the postoperative prognosis in patients with HBV-related HCC after liver resection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Postoperative Albumin-Bilirubin Grade Change Predicts the Prognosis of Patients with Hepatitis B-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma Within the Milan Criteria.World J Surg. 2018 Jun;42(6):1841-1847. doi: 10.1007/s00268-017-4355-2. World J Surg. 2018. PMID: 29138913
-
Preoperative albumin-bilirubin grade combined with aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet count ratio index predict outcomes of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma within Milan criteria after liver resection.Biosci Trends. 2019 May 12;13(2):176-181. doi: 10.5582/bst.2019.01088. Epub 2019 Apr 27. Biosci Trends. 2019. PMID: 31061272
-
Albumin-bilirubin and platelet-albumin-bilirubin grades for hepatitis B-associated hepatocellular carcinoma in Child-Pugh A patients treated with radical surgery: A retrospective observational study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Oct;98(43):e17394. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000017394. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31651841 Free PMC article.
-
Management of hepatitis B virus infection during treatment for hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Jul 21;21(27):8249-55. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i27.8249. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26217076 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of the Albumin-Bilirubin Grade in Predicting the Prognosis of Patients With Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Transplant Proc. 2019 Dec;51(10):3338-3346. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2019.08.027. Epub 2019 Nov 13. Transplant Proc. 2019. PMID: 31732203
Cited by
-
Albumin-bilirubin index and platelet-albumin-bilirubin index contribute to identifying survival benefit candidates in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and Child-Pugh grade A undergoing transcatheter arterial chemoembolization with sorafenib treatment.Ann Transl Med. 2021 Feb;9(3):237. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-3118. Ann Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 33708864 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of pretreatment albumin to bilirubin ratio in patients with hepatocellular cancer: A meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Jan;98(2):e14027. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000014027. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 30633195 Free PMC article.
-
Albumin-Bilirubin Grade Analyses of Atezolizumab plus Bevacizumab versus Sorafenib in Patients with Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Post Hoc Analysis of the Phase III IMbrave150 Study.Liver Cancer. 2023 Mar 4;12(5):479-493. doi: 10.1159/000529996. eCollection 2023 Oct. Liver Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37901766 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Value of Platelet-Albumin-Bilirubin Grade in Child-Pugh A and B Patients With Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis.Front Oncol. 2022 Jul 13;12:914997. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.914997. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35912198 Free PMC article.
-
Albumin-Bilirubin Score Differentiates Liver Fibrosis Stage and Hepatocellular Carcinoma Incidence in Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection: A Retrospective Cohort Study.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2019 Jul;101(1):220-225. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.19-0129. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2019. PMID: 31115300 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 2015;65:87–108. - PubMed
-
- de Haas RJ, Lim C, Bhangui P, et al. Curative salvage liver transplantation in cirrhotic patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: an intention-to-treat analysis. Hepatology 2017;67:204–15. - PubMed
-
- Wang YY, Zhong JH, Su ZY, et al. Albumin-bilirubin versus Child–Pugh score as a predictor of outcome after liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Surg 2016;103:725–34. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

