The dual CCR2/CCR5 chemokine receptor antagonist Cenicriviroc reduces macrophage infiltration and disease severity in Duchenne muscular dystrophy (Dmdmdx-4Cv) mice
- PMID: 29561896
- PMCID: PMC5862483
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0194421
The dual CCR2/CCR5 chemokine receptor antagonist Cenicriviroc reduces macrophage infiltration and disease severity in Duchenne muscular dystrophy (Dmdmdx-4Cv) mice
Abstract
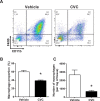
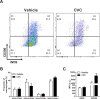
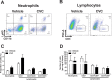
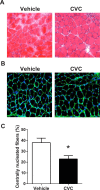
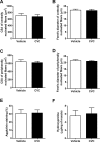
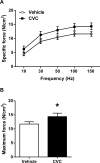
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is characterized by progressive muscle weakness which is ultimately fatal, most often due to involvement of the diaphragm. Macrophage infiltration of dystrophic muscles has been strongly linked to muscle damage and fibrosis in DMD. We hypothesized that cenicriviroc (CVC), a dual chemokine receptor (CCR2/CCR5) antagonist currently under clinical evaluation for other diseases, could prevent macrophage accumulation and blunt disease progression in the diaphragms of mdx mice (genetic homologue of DMD). Treatment with CVC (20 mg/kg/day intraperitoneally) or vehicle was initiated in mdx mice at 2 weeks of age (prior to the onset of muscle necrosis) and continued for 4 weeks. Flow cytometry to assess inflammatory cell subsets as well as histological and force generation parameters were determined in mdx diaphragms at the conclusion of the treatment. CVC therapy induced a major (3.9-fold) reduction in total infiltrating macrophages, whereas total numbers of neutrophils and T lymphocytes (CD4+ and CD8+) were unaffected. No changes in macrophage polarization status (inflammatory versus anti-inflammatory skewing based on iNOS and CD206 expression) were observed. Muscle fiber size and fibrosis were not altered by CVC, whereas a significant reduction in centrally nucleated fibers was found suggesting a decrease in prior necrosis-regeneration cycles. In addition, maximal isometric force production by the diaphragm was increased by CVC therapy. These results suggest that CVC or other chemokine receptor antagonists which reduce pathological macrophage infiltration may have the potential to slow disease progression in DMD.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Mah JK, Korngut L, Dykeman J, Day L, Pringsheim T, Jette N. A systematic review and meta-analysis on the epidemiology of Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy. Neuromuscul Disord. 2014;24: 482–91. doi: 10.1016/j.nmd.2014.03.008 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Manzur AY, Kuntzer T, Pike M, Swan A. Glucocorticoid corticosteroids for Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Cochrane database Syst Rev. 2008; CD003725 doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003725.pub3 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Acharyya S, Villalta SA, Bakkar N, Bupha-Intr T, Janssen PML, Carathers M, et al. Interplay of IKK/NF-kappaB signaling in macrophages and myofibers promotes muscle degeneration in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. J Clin Invest. 2007;117: 889–901. doi: 10.1172/JCI30556 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wehling M, Spencer MJ, Tidball JG. A nitric oxide synthase transgene ameliorates muscular dystrophy in mdx mice. J Cell Biol. 2001;155: 123–131. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200105110 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sica A, Mantovani A. Macrophage plasticity and polarization: in vivo veritas. J Clin Invest. 2012;122: 787–795. doi: 10.1172/JCI59643 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

