Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab versus Sunitinib in Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 29562145
- PMCID: PMC5972549
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1712126
Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab versus Sunitinib in Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Nivolumab plus ipilimumab produced objective responses in patients with advanced renal-cell carcinoma in a pilot study. This phase 3 trial compared nivolumab plus ipilimumab with sunitinib for previously untreated clear-cell advanced renal-cell carcinoma.
Methods: We randomly assigned adults in a 1:1 ratio to receive either nivolumab (3 mg per kilogram of body weight) plus ipilimumab (1 mg per kilogram) intravenously every 3 weeks for four doses, followed by nivolumab (3 mg per kilogram) every 2 weeks, or sunitinib (50 mg) orally once daily for 4 weeks (6-week cycle). The coprimary end points were overall survival (alpha level, 0.04), objective response rate (alpha level, 0.001), and progression-free survival (alpha level, 0.009) among patients with intermediate or poor prognostic risk.
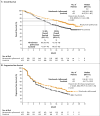
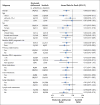
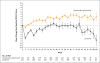
Results: A total of 1096 patients were assigned to receive nivolumab plus ipilimumab (550 patients) or sunitinib (546 patients); 425 and 422, respectively, had intermediate or poor risk. At a median follow-up of 25.2 months in intermediate- and poor-risk patients, the 18-month overall survival rate was 75% (95% confidence interval [CI], 70 to 78) with nivolumab plus ipilimumab and 60% (95% CI, 55 to 65) with sunitinib; the median overall survival was not reached with nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus 26.0 months with sunitinib (hazard ratio for death, 0.63; P<0.001). The objective response rate was 42% versus 27% (P<0.001), and the complete response rate was 9% versus 1%. The median progression-free survival was 11.6 months and 8.4 months, respectively (hazard ratio for disease progression or death, 0.82; P=0.03, not significant per the prespecified 0.009 threshold). Treatment-related adverse events occurred in 509 of 547 patients (93%) in the nivolumab-plus-ipilimumab group and 521 of 535 patients (97%) in the sunitinib group; grade 3 or 4 events occurred in 250 patients (46%) and 335 patients (63%), respectively. Treatment-related adverse events leading to discontinuation occurred in 22% and 12% of the patients in the respective groups.
Conclusions: Overall survival and objective response rates were significantly higher with nivolumab plus ipilimumab than with sunitinib among intermediate- and poor-risk patients with previously untreated advanced renal-cell carcinoma. (Funded by Bristol-Myers Squibb and Ono Pharmaceutical; CheckMate 214 ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT02231749 .).
Conflict of interest statement
No other potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Comment in
-
Immunotherapy in Advanced Renal Cancer - Is Cure Possible?N Engl J Med. 2018 Apr 5;378(14):1344-1345. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1801682. Epub 2018 Mar 21. N Engl J Med. 2018. PMID: 29562143 No abstract available.
-
Kidney cancer: Antibody pincer movement challenges sunitinib as standard therapy.Nat Rev Urol. 2018 May;15(5):261. doi: 10.1038/nrurol.2018.47. Epub 2018 Apr 10. Nat Rev Urol. 2018. PMID: 29632348 No abstract available.
-
CheckMate 214 - a winning combination?Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2018 Jun;15(6):343. doi: 10.1038/s41571-018-0020-4. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29666439 No abstract available.
-
Immune Checkpoint Blockade in Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma.N Engl J Med. 2018 Jul 5;379(1):91-2. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1805988. N Engl J Med. 2018. PMID: 29975027 No abstract available.
-
Re: Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab Versus Sunitinib in Advanced Renal-cell Carcinoma.Eur Urol. 2018 Nov;74(5):679-680. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2018.07.019. Epub 2018 Aug 10. Eur Urol. 2018. PMID: 30104083 No abstract available.
-
Frontline immunotherapy treatment with nivolumab and ipilimumab in metastatic renal cell cancer: a new standard of care.Cancer Biol Ther. 2019;20(1):6-7. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2018.1507260. Epub 2018 Oct 17. Cancer Biol Ther. 2019. PMID: 30332546 Free PMC article.
-
Fortgeschrittenes Nierenzellkarzinom: Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab versus Sunitinib.Aktuelle Urol. 2019 Apr;50(2):136. doi: 10.1055/a-0603-7847. Epub 2019 Mar 21. Aktuelle Urol. 2019. PMID: 30897630 German. No abstract available.
-
Immune Checkpoint Blockade plus Axitinib for Renal-Cell Carcinoma.N Engl J Med. 2019 Jun 27;380(26):2581. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1905518. N Engl J Med. 2019. PMID: 31242369 No abstract available.
-
Immune Checkpoint Blockade plus Axitinib for Renal-Cell Carcinoma. Reply.N Engl J Med. 2019 Jun 27;380(26):2582. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1905518. N Engl J Med. 2019. PMID: 31242371 No abstract available.
References
-
- Motzer RJ, Jonasch E, Agarwal N, et al. Kidney cancer, version 2.2017, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2017;15:804–34. - PubMed
-
- Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Cella D, et al. Pazopanib versus sunitinib in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:722–31. - PubMed
-
- Choueiri TK, Motzer RJ. Systemic therapy for metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2017;376:354–66. - PubMed
-
- Heng DY, Xie W, Regan MM, et al. Prognostic factors for overall survival in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted agents: results from a large, multicenter study. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:5794–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
