Autoimmune Polyendocrine Syndromes
- PMID: 29562162
- PMCID: PMC6007870
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMra1713301
Autoimmune Polyendocrine Syndromes
Figures
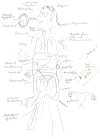

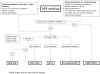
Comment in
-
Autoimmune Polyendocrine Syndromes.N Engl J Med. 2018 Jun 28;378(26):2542-3. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1805308. N Engl J Med. 2018. PMID: 29952181 No abstract available.
-
Autoimmune Polyendocrine Syndromes.N Engl J Med. 2018 Jun 28;378(26):2543. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1805308. N Engl J Med. 2018. PMID: 29952183 No abstract available.
References
-
- Schmidt MB. Eine biglandulare Erkrankung (Nebennieren und Schilddrüse) bei Morbus Adisonii. Verh Dtsch Ges Pathol. 1926;21:212–21.
-
- An autoimmune disease, APECED, caused by mutations in a novel gene featuring two PHD-type zinc-finger domains. The Finnish-German APECED Consortium. Autoimmune Polyendocrinopathy-Candidiasis-Ectodermal Dystrophy. Nat Genet. 1997;17:399–403. - PubMed
-
- Nagamine K, Peterson P, Scott HS, et al. Positional cloning of the APECED gene. Nat Genet. 1997;17:393–8. - PubMed
-
- Husebye ES, Perheentupa J, Rautemaa R, Kampe O. Clinical manifestations and management of patients with autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type I. J Intern Med. 2009;265:514–29. - PubMed
-
- Ahonen P, Myllarniemi S, Sipila I, Perheentupa J. Clinical variation of autoimmune polyendocrinopathy-candidiasis-ectodermal dystrophy (APECED) in a series of 68 patients. N Engl J Med. 1990;322:1829–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
