Vedolizumab as Induction and Maintenance for Inflammatory Bowel Disease: 12-month Effectiveness and Safety
- PMID: 29562271
- PMCID: PMC6196763
- DOI: 10.1093/ibd/izx067
Vedolizumab as Induction and Maintenance for Inflammatory Bowel Disease: 12-month Effectiveness and Safety
Abstract
Background: Vedolizumab is approved for moderate to severe Crohn's disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC). We present prospective, 1-year data of the real-world effectiveness and safety of vedolizumab in inflammatory bowel disease.
Methods: Consecutive patients receiving vedolizumab for treatment of UC or CD with at least 14 weeks of follow-up, regardless of outcome, were included. Patients had clinical activity scores (Harvey-Bradshaw Index [HBI] or Simple Clinical Colitis Activity Index [SCCAI]) and inflammatory markers prospectively measured at baseline and weeks 14, 30, and 52. Clinical response was defined as a reduction ≥3 in HBI or SCCAI, clinical remission as HBI ≤4 or SCCAI ≤2, steroid-free remission as clinical remission without the need for corticosteroids, and mucosal healing (assessed at 6 months) as a Mayo endoscopic subscore of 0 or 1 or CD-SES <3.
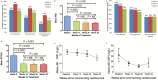
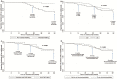
Results: A total of 132 patients were included: 61 (45%) male, 94 (71%) with CD, 42 (29%) with UC; 22% and 34% of CD and UC patients, respectively, achieved steroid-free remission by week 14. This increased to 31% in CD patients and plateaued at 35% in UC patients at 12 months. Increasing remission rates to 6 months were seen in patients with CD, but minimal improvements after 3 months of therapy occurred in those with UC. Mucosal healing was achieved in 52% of UC and 30% of CD patients. Most adverse events were minor; 74% remained on vedolizumab at 12 months.
Conclusions: In this real-world study, vedolizumab demonstrated similar efficacy and safety seen in pivotal trials, with sustained clinical response in the majority of patients. Similar rates of response were seen in UC and CD patients. 10.1093/ibd/izx067_video1izx067_Video5754037470001.
Figures

References
-
- Lichtenstein GR, Hanauer SB, Sandborn WJ; Practice Parameters Committee of American College of Gastroenterology Management of Crohn’s disease in adults. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009;104:465–83; quiz 464, 484. - PubMed
-
- Bonovas S, Fiorino G, Allocca M et al. . Biologic therapies and risk of infection and malignancy in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;14:1385–397.e10. - PubMed
-
- Lobatón T, Vermeire S, Van Assche G et al. . Review article: anti-adhesion therapies for inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2014;39:579–94. - PubMed
-
- Feagan BG, Rutgeerts P, Sands BE et al. ; GEMINI 1 Study Group Vedolizumab as induction and maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:699–710. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

