Balanced scorecard-based performance evaluation of Chinese county hospitals in underdeveloped areas
- PMID: 29562812
- PMCID: PMC5991253
- DOI: 10.1177/0300060518757606
Balanced scorecard-based performance evaluation of Chinese county hospitals in underdeveloped areas
Abstract
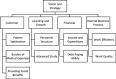
Objective Since the Guangxi government implemented public county hospital reform in 2009, there have been no studies of county hospitals in this underdeveloped area of China. This study aimed to establish an evaluation indicator system for Guangxi county hospitals and to generate recommendations for hospital development and policymaking. Methods A performance evaluation indicator system was developed based on balanced scorecard theory. Opinions were elicited from 25 experts from administrative units, universities and hospitals and the Delphi method was used to modify the performance indicators. The indicator system and the Topsis method were used to evaluate the performance of five county hospitals randomly selected from the same batch of 2015 Guangxi reform pilots. Results There were 4 first-level indicators, 9 second-level indicators and 36 third-level indicators in the final performance evaluation indicator system that showed good consistency, validity and reliability. The performance rank of the hospitals was B > E > A > C > D. Conclusions The performance evaluation indicator system established using the balanced scorecard is practical and scientific. Analysis of the results based on this indicator system identified several factors affecting hospital performance, such as resource utilisation efficiency, medical service price, personnel structure and doctor-patient relationships.
Keywords: China; County hospital; balanced scorecard; indicator system; medically underserved area; performance evaluation.
Figures
References
-
- Opinions of the CPC Central Committee and the State Council on Deepening the Health Care System Reform. The Central People's Government of the People's Republic of China Website. http://www.gov.cn/test/2009-04/08/content_1280069.htm. Published March 17, 2009. Accessed February 5, 2017.
-
- Implementation Plan for the Recent Priorities of the Health Care System Reform ( 2009. –2011). The Central People's Government of the People's Republic of China Website. http://www.gov.cn/zwgk/2009-04/07/content_1279256.htm. Published March 18, 2009. Accessed February 5, 2017.
-
- Opinions of Pilot Projects for County-level Public Hospital Reform. The Central People's Government of the People's Republic of China Website. http://www.gov.cn/zwgk/2012-06/14/content_2161153.htm. Published June 7, 2012. Accessed February 5, 2017.
-
- Kaplan RS andNorton DP.. The balanced scorecard–measures that drive performance. Harv Bus Rev 1992; 70: 70–79. - PubMed
-
- Madsen D andSlåtten K.. The role of the management fashion arena in the cross-national diffusion of management concepts: the case of the balanced scorecard in the Scandinavian countries. Adm Sci 2013; 3: 110–142.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources