Effects of prescribed aerobic exercise volume on physical activity and sedentary time in postmenopausal women: a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 29562927
- PMCID: PMC5863375
- DOI: 10.1186/s12966-018-0659-3
Effects of prescribed aerobic exercise volume on physical activity and sedentary time in postmenopausal women: a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Physical activity has emerged as an important lifestyle factor for primary prevention of numerous diseases, including postmenopausal breast cancer. No study to date has assessed the acute and long-term effects of year-long aerobic exercise programs differing in prescribed exercise volume on physical activity and sedentary time in postmenopausal women. Therefore, we aimed to examine the effects of two moderate-vigorous intensity exercise doses on total, light and moderate-vigorous intensity physical activity times, and sedentary time in postmenopausal women during the year-long intervention and one year later.
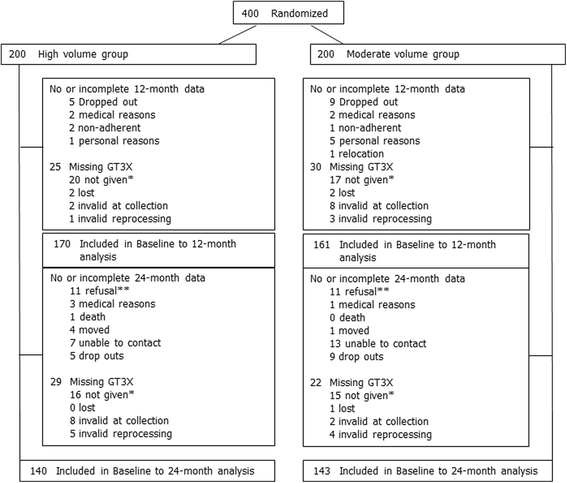
Methods: The Breast Cancer and Exercise Trial in Alberta (BETA) was a two-center, two-arm, 12-month randomized controlled trial that included 400 previously inactive postmenopausal women randomized to either 150 (MODERATE) or 300 (HIGH) minutes/week of aerobic exercise. Physical activity and sedentary time were assessed at baseline, 6- (intervention mid-point), 12- (prior to end of intervention) and 24-months (follow-up) with waist-mounted accelerometers (Actigraph GTX3®). Self-reported activity and sedentary time at baseline, 12- and 24-months was also assessed (Past Year Total Physical Activity Questionnaire and SIT-Q). Intention-to-treat analyses were conducted using linear mixed models and adjusted for baseline variables.
Results: Both physical activity interventions led to increases in objective and subjective measures of total and moderate-vigorous intensity/recreational physical activity time, coupled with decreases in sedentary time, at 6- and 12-months compared to baseline. Additionally, greater increases in accelerometry-derived total physical activity time at 6- and 12-months, and self-reported recreational activity time at 12-months, compared to baseline were noted in the HIGH versus MODERATE groups. Decreases in total, light and moderate-vigorous intensity physical activity time, and an increase in sedentary time, in both groups were noted at 24-months compared to 12-months. A decrease in light intensity physical activity time in both groups at 24-months compared to baseline was also noted.
Conclusion: These findings have important health implications, suggesting that total physical activity time can be increased with greater volumes of prescribed exercise, but that additional support and resources could be used to promote the maintenance of these high levels of aerobic exercise participation following study completion.
Trial registration: clinicaltrials.gov identifier: NCT01435005 (BETA Trial). Registred September 15th 2011 (retrospectively registered).
Keywords: Exercise dose; Exercise intervention; Follow-up; Sedentary behavior.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study protocol was approved by the Alberta Cancer Research Ethics Committee, the Conjoint Health Research Ethics Board of the University of Calgary and the Health Research Ethics Board of the University of Alberta. Informed consent was provided by all participants prior to study participation.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Perk J, De Backer G, Gohlke H, Graham I, Reiner Z, Verschuren M, Albus C, Benlian P, Boysen G, Cifkova R, et al. European guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice (version 2012). The fifth joint task force of the European Society of Cardiology and Other Societies on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice (constituted by representatives of nine societies and by invited experts) Eur Heart J. 2012;33:1635–1701. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehs092. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Moore SC, Lee IM, Weiderpass E, Campbell PT, Sampson JN, Kitahara CM, Keadle SK, Arem H, Berrington de Gonzalez A, Hartge P, et al. Association of leisure-time physical activity with risk of 26 types of cancer in 1.44 million adults. JAMA Intern Med. 2016;176:816–825. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2016.1548. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

