Effectiveness of urine fibronectin as a non-invasive diagnostic biomarker in bladder cancer patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 29562940
- PMCID: PMC5863379
- DOI: 10.1186/s12957-018-1358-x
Effectiveness of urine fibronectin as a non-invasive diagnostic biomarker in bladder cancer patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Previous researches pointed out that the measurement of urine fibronectin (Fn) could be a potential diagnostic test for bladder cancer (BCa). We conducted this meta-analysis to fully assess the diagnostic value of urine Fn for BCa detection.
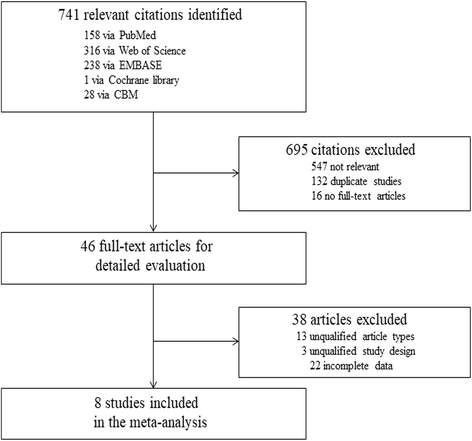
Methods: A systematic literature search in PubMed, ISI Web of Science, EMBASE, Cochrane library, and CBM was carried out to identify eligible studies evaluating the urine Fn in diagnosing BCa. Pooled sensitivity, specificity, and diagnostic odds ratio (DOR) with their 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated, and summary receiver operating characteristic (SROC) curves were established. We applied the STATA 13.0, Meta-Disc 1.4, and RevMan 5.3 software to the meta-analysis.
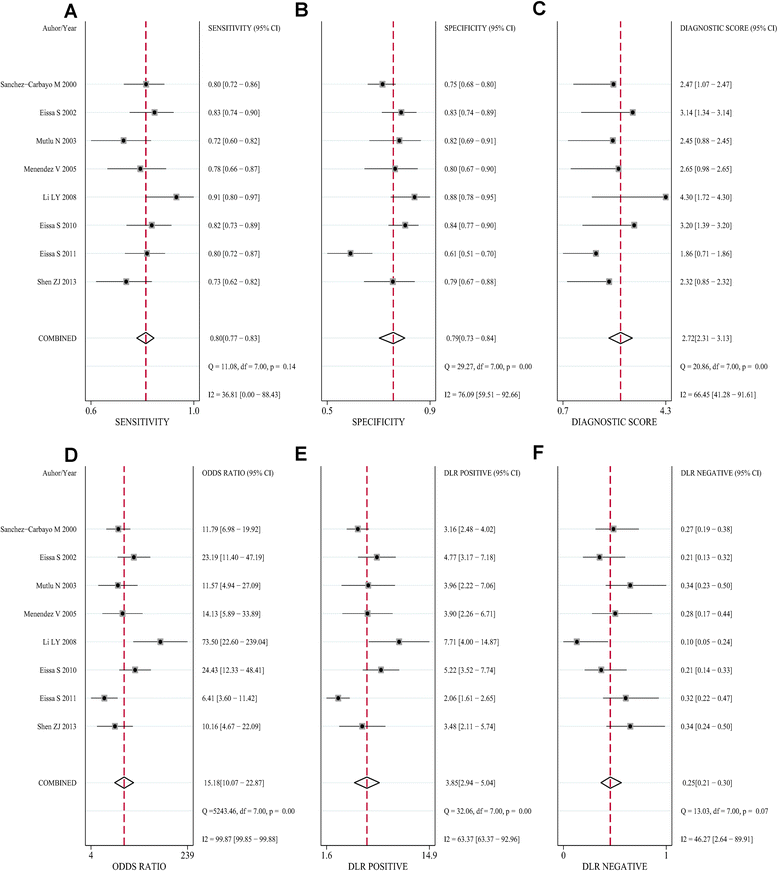
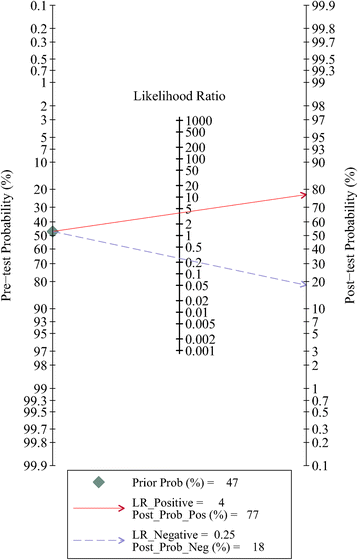
Results: Eight separate studies with 744 bladder cancer patients were enrolled in this meta-analysis. The pooled sensitivity, specificity, and DOR were 0.80 (95%CI = 0.77-0.83), 0.79 (95%CI = 0.73-0.84), and 15.18 (95%CI = 10.07-22.87), respectively, and the area under the curve (AUC) of SROC was 0.83 (95%CI = 0.79-0.86). The diagnostic power of a combined method (urine Fn combined with urine cytology) was also evaluated, and its sensitivity and AUC were significantly higher (0.86 (95%CI = 0.82-0.90) and 0.89 (95%CI = 0.86-0.92), respectively). Meta-regression along with subgroup analysis based on various covariates revealed the potential sources of the heterogeneity and the detailed diagnostic value of each subgroup. Sensitivity analysis supported that the result was robust. No threshold effect and publication bias were found in this meta-analysis.
Conclusions: Urine Fn may become a promising non-invasive biomarker for bladder cancer with a relatively satisfactory diagnostic power. And the combination of urine Fn with cytology could be an alternative option for detecting BCa in clinical practice. The potential value of urine Fn still needs to be validated in large, multi-center, and prospective studies.
Keywords: Biomarker; Bladder cancer; Diagnosis; Meta-analysis; Urine fibronectin.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
In accordance with the ethical standards of institutional and international research committee, this article is based on previous published studies; thus, it does not contain any studies with human participants or animals.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic review and evaluation of methods of assessing urinary incontinence.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Feb;10(6):1-132, iii-iv. doi: 10.3310/hta10060. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16487456
-
Structural alterations of sugar chains in urine fibronectin from bladder cancer patients and its enzymatic mechanism.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2001 Aug;127(8):512-9. doi: 10.1007/s004320100245. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2001. PMID: 11501752 Free PMC article.
-
Doppler trans-thoracic echocardiography for detection of pulmonary hypertension in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 9;5(5):CD012809. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012809.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35532166 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic tests and algorithms used in the investigation of haematuria: systematic reviews and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Jun;10(18):iii-iv, xi-259. doi: 10.3310/hta10180. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16729917
Cited by
-
Integrative analysis of Anoikis-related genes reveals that FASN is a novel prognostic biomarker and promotes the malignancy of bladder cancer via Wnt/β-catenin pathway.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 3;10(13):e34029. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34029. eCollection 2024 Jul 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39071712 Free PMC article.
-
Ureteral involvement by metastatic malignant disease.Clin Exp Metastasis. 2019 Dec;36(6):499-509. doi: 10.1007/s10585-019-09989-8. Epub 2019 Aug 24. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2019. PMID: 31446521
-
Fibronectin urothelial gene expression as a new reliable biomarker for early detection of local toxicity secondary to adjuvant intravesical therapy for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer.Ther Adv Urol. 2021 Feb 27;13:1756287221995683. doi: 10.1177/1756287221995683. eCollection 2021 Jan-Dec. Ther Adv Urol. 2021. PMID: 33717214 Free PMC article.
-
Significance of fibulin-3 expression in bladder cancer: a tissue microarray-based immunohistochemical study.World J Surg Oncol. 2022 Apr 26;20(1):133. doi: 10.1186/s12957-022-02597-z. World J Surg Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35473807 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Surface Plasmon Resonance Imaging Biosensors for Determination of Fibronectin, Laminin-5, and Type IV Collagen in Plasma, Urine, and Tissue of Renal Cell Carcinoma.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Sep 30;24(19):6371. doi: 10.3390/s24196371. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39409411 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sagerman PM, Saigo PE, Sheinfeld J, Charitonowics E, Cordon-Cardo C. Enhanced detection of bladder cancer in urine cytology with Lewis X, M344 and 19A211 antigens. Acta Cytol. 1994;38:517–523. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

