Opioid Rotation in Cancer Pain Treatment
- PMID: 29563006
- PMCID: PMC5876542
- DOI: 10.3238/arztebl.2018.0135
Opioid Rotation in Cancer Pain Treatment
Abstract
Background: Rotating several different WHO level III opioid drugs is a therapeutic option for patients with chronic cancer-related pain who suffer from inadequate analgesia and/or intolerable side effects. The evidence favoring opioid rotation is controversial, and the current guidelines in Germany and other countries contain only weak recommendations for it.
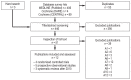
Methods: This review is based on pertinent publications retrieved by a systematic review of the literature on opioid rotation for adult patients with chronic cancerrelated pain who are regularly taking WHO level III opioids by the oral or trans - dermal route.
Results: 9 individual studies involving a total of 725 patients were included in the analysis, and 3 previous systematic reviews of studies involving a total of 2296 patients were also analyzed. Morphine, oxycodone, fentanyl, hydromorphone, and buprenorphine were used as first-line opioid drugs, and hydromorphone, bupre - norphine, tapentadol, fentanyl, morphine, oxymorphone, and methadone were used as second-line opioid drugs. In all of the studies, pain control was achieved for 14 days after each rotation. In most of them, the dose of the new drug introduced in each rotation needed to be increased above the dose initially calculated from a rotation ratio, with the exception of rotations to methadone. The frequency of side effects was only rarely lessened, but patients largely considered the result of opioid rotation to be positive. No particular opioid drug was found to be best.
Conclusion: Opioid rotation can improve analgesia and patient satisfaction. The success of opioid rotation appears to depend on the magnitude of the initial dose, among other factors. Tables of equianalgesic doses should be considered no more than a rough guide for determining the dose of the new drug. Rotations to methadone should be carried out under clinical supervision in experienced hands.
References
-
- Bruera ED, Portenoy RK. Cambridge University Press. 2. New York: 2010. Cancer pain Assessment and management.
-
- Meuser T, Pietruck C, Radbruch L, Stute P, Lehmann KA, Grond S. Symptoms during cancer pain treatment following WHO-guidelines: a longitudinal follow-up study of symptom prevalence, severity and etiology. Pain. 2001;93:247–257. - PubMed
-
- Nalamachu SR. Opioid rotation in clinical practice. Adv Ther. 2012;29:849–863. - PubMed
-
- Knotkova H, Fine PG, Portenoy RK. Opioid rotation: the science and the limitations of the equianalgesic dose table. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2009;38:426–439. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical