Paraquat initially damages cochlear support cells leading to anoikis-like hair cell death
- PMID: 29563067
- PMCID: PMC5984146
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heares.2018.03.014
Paraquat initially damages cochlear support cells leading to anoikis-like hair cell death
Abstract
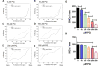
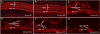
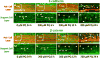
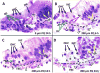
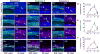
Paraquat (PQ), one of the most widely used herbicides, is extremely dangerous because it generates the highly toxic superoxide radical. When paraquat was applied to cochlear organotypic cultures, it not only damaged the outer hair cells (OHCs) and inner hair cells (IHCs), but also caused dislocation of the hair cell rows. We hypothesized that the dislocation arose from damage to the support cells (SCs) that anchors hair cells within the epithelium. To test this hypothesis, rat postnatal cochlear cultures were treated with PQ. Shortly after PQ treatment, the rows of OHCs separated from one another and migrated radially away from IHCs suggesting loss of cell-cell adhesion that hold the hair cells in proper alignment. Hair cells dislocation was associated with extensive loss of SCs in the organ of Corti, loss of tympanic border cells (TBCs) beneath the basilar membrane, the early appearance of superoxide staining and caspase-8 labeling in SCs below the OHCs and disintegration of E-cadherin and β-catenin in the organ of Corti. Damage to the TBCs and SCs occurred prior to loss of OHC or IHC loss suggesting a form of detachment-induced apoptosis referred to as anoikis.
Keywords: Anoikis; Caspase-8; E-cadherin; Paraquat; Superoxide; β-catenin.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
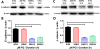
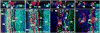

References
-
- Anderson KD, Scerri GV. A case of multiple skin cancers after occupational exposure to pesticides. Br J Dermatol. 2003;149:1088–9. - PubMed
-
- Assreuy J, Cunha FQ, Epperlein M, Noronha-Dutra A, O’Donnell CA, Liew FY, Moncada S. Production of nitric oxide and superoxide by activated macrophages and killing of Leishmania major. Eur J Immunol. 1994;24:672–6. - PubMed
-
- Baltazar MT, Dinis-Oliveira RJ, de Lourdes Bastos M, Tsatsakis AM, Duarte JA, Carvalho F. Pesticides exposure as etiological factors of Parkinson’s disease and other neurodegenerative diseases–a mechanistic approach. Toxicol Lett. 2014;230:85–103. - PubMed
-
- Berry C, La Vecchia C, Nicotera P. Paraquat and Parkinson’s disease. Cell Death Differ. 2010;17:1115–25. - PubMed
-
- Bertsias GK, Katonis P, Tzanakakis G, Tsatsakis AM. Review of clinical and toxicological features of acute pesticide poisonings in Crete (Greece) during the period 1991-2001. Med Sci Monit. 2004;10:CR622–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

