Laboratory-confirmed respiratory infections as triggers for acute myocardial infarction and stroke: a self-controlled case series analysis of national linked datasets from Scotland
- PMID: 29563170
- PMCID: PMC5898931
- DOI: 10.1183/13993003.01794-2017
Laboratory-confirmed respiratory infections as triggers for acute myocardial infarction and stroke: a self-controlled case series analysis of national linked datasets from Scotland
Abstract
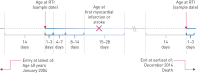
While acute respiratory tract infections can trigger cardiovascular events, the differential effect of specific organisms is unknown. This is important to guide vaccine policy.Using national infection surveillance data linked to the Scottish Morbidity Record, we identified adults with a first myocardial infarction or stroke from January 1, 2004 to December 31, 2014 and a record of laboratory-confirmed respiratory infection during this period. Using self-controlled case series analysis, we generated age- and season-adjusted incidence ratios (IRs) for myocardial infarction (n=1227) or stroke (n=762) after infections compared with baseline time.We found substantially increased myocardial infarction rates in the week after Streptococcus pneumoniae and influenza virus infection: adjusted IRs for days 1-3 were 5.98 (95% CI 2.47-14.4) and 9.80 (95% CI 2.37-40.5), respectively. Rates of stroke after infection were similarly high and remained elevated to 28 days: day 1-3 adjusted IRs 12.3 (95% CI 5.48-27.7) and 7.82 (95% CI 1.07-56.9) for S. pneumoniae and influenza virus, respectively. Although other respiratory viruses were associated with raised point estimates for both outcomes, only the day 4-7 estimate for stroke reached statistical significance.We showed a marked cardiovascular triggering effect of S. pneumoniae and influenza virus, which highlights the need for adequate pneumococcal and influenza vaccine uptake. Further research is needed into vascular effects of noninfluenza respiratory viruses.
Copyright ©ERS 2018.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: H. Whitaker has received grants from the MRC (methodology grant MR/L009005/1) and IMI/EFPIA (ADVANCE), outside the submitted work.
Figures
Comment in
-
The Baffling Case of Ischemic Stroke Disappearance from the Casualty Department in the COVID-19 Era.Eur Neurol. 2020;83(2):213-215. doi: 10.1159/000507666. Epub 2020 Apr 14. Eur Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32289789 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- World Health Organization. The top 10 causes of death. www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs310/en/index.html Date last accessed: July 20, 2017. Date last updated: January, 2017.
-
- Warren-Gash C, Smeeth L, Hayward AC. Influenza as a trigger for acute myocardial infarction or death from cardiovascular disease: a systematic review. Lancet Infect Dis 2009; 9: 601–610. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
