Relative Contributions of B Cells and Dendritic Cells from Lupus-Prone Mice to CD4+ T Cell Polarization
- PMID: 29563177
- PMCID: PMC5915918
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1701179
Relative Contributions of B Cells and Dendritic Cells from Lupus-Prone Mice to CD4+ T Cell Polarization
Abstract
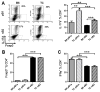
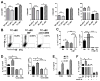
Mouse models of lupus have shown that multiple immune cell types contribute to autoimmune disease. This study sought to investigate the involvement of B cells and dendritic cells in supporting the expansion of inflammatory and regulatory CD4+ T cells that are critical for lupus pathogenesis. We used lupus-prone B6.NZM2410.Sle1.Sle2.Sle3 (TC) and congenic C57BL/6J (B6) control mice to investigate how the genetic predisposition of these two cell types controls the activity of normal B6 T cells. Using an allogeneic in vitro assay, we showed that TC B1-a and conventional B cells expanded Th17 cells significantly more than their B6 counterparts. This expansion was dependent on CD86 and IL-6 expression and mapped to the Sle1 lupus-susceptibility locus. In vivo, TC B cells promoted greater differentiation of CD4+ T cells into Th1 and follicular helper T cells than did B6 B cells, but they limited the expansion of Foxp3 regulatory CD4+ T cells to a greater extent than did B6 B cells. Finally, when normal B6 CD4+ T cells were introduced into Rag1-/- mice, TC myeloid/stromal cells caused their heightened activation, decreased Foxp3 regulatory CD4+ T cell differentiation, and increased renal infiltration of Th1 and Th17 cells in comparison with B6 myeloid/stromal cells. The results show that B cells from lupus mice amplify inflammatory CD4+ T cells in a nonredundant manner with myeloid/stromal cells.
Copyright © 2018 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Mariño E, Grey ST. B cells as effectors and regulators of autoimmunity. Autoimmunity. 2012;45:377–387. - PubMed
-
- Vinuesa CG, Sanz I, Cook MC. Dysregulation of germinal centres in autoimmune disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2009;9:845–857. - PubMed
-
- Blanco P, Ueno H, Schmitt N. T follicular helper (Tfh) cells in lupus: Activation and involvement in SLE pathogenesis. Eur J Immunol. 2016;46:281–290. - PubMed
-
- Sozzani S, Del Prete A, Bosisio D. Dendritic cell recruitment and activation in autoimmunity. J Autoimmun. 2017;85:126–140. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

