Multicenter Validation of Commercial Antigenuria Reagents To Diagnose Progressive Disseminated Histoplasmosis in People Living with HIV/AIDS in Two Latin American Countries
- PMID: 29563205
- PMCID: PMC5971531
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.01959-17
Multicenter Validation of Commercial Antigenuria Reagents To Diagnose Progressive Disseminated Histoplasmosis in People Living with HIV/AIDS in Two Latin American Countries
Abstract
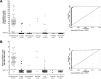
Histoplasmosis is an important cause of mortality in patients with AIDS, especially in countries with limited access to antiretroviral therapies and diagnostic tests. However, many disseminated infections in Latin America go undiagnosed. A simple, rapid method to detect Histoplasma capsulatum infection in regions where histoplasmosis is endemic would dramatically decrease the time to diagnosis and treatment, reducing morbidity and mortality. The aim of this study was to validate a commercial monoclonal Histoplasma galactomannan (HGM) enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (Immuno-Mycologics [IMMY], Norman, OK, USA) in two cohorts of people living with HIV/AIDS (PLHIV). We analyzed urine samples from 589 people (466 from Guatemala and 123 from Colombia), including 546 from PLHIV and 43 from non-PLHIV controls. Sixty-three of these people (35 from Guatemala and 28 from Colombia) had confirmed histoplasmosis by isolation of H. capsulatum Using the standard curve provided by the quantitative commercial test, the sensitivity was 98% (95% confidence interval [CI], 95 to 100%) and the specificity was 97% (95% CI, 96 to 99%) (cutoff = 0.5 ng/ml). Semiquantitative results, using a calibrator of 12.5 ng/ml of Histoplasma galactomannan to calculate an enzyme immunoassay index value (EIV) for the samples, showed a sensitivity of 95% (95% CI, 89 to 100%) and a specificity of 98% (95% CI, 96 to 99%) (cutoff ≥ 2.6 EIV). This relatively simple-to-perform commercial antigenuria test showed a high performance with reproducible results in both countries, suggesting that it can be used to detect progressive disseminated histoplasmosis in PLHIV in a wide range of clinical laboratories in countries where histoplasmosis is endemic.
Keywords: AIDS; ELISA; Histoplasma capsulatum; antigen; histoplasmosis.
Copyright © 2018 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
References
-
- Tobon A, Gomez BL. 2015. Histoplasmosis. In Vesga O, Vélez LA, Leiderman E, Restrepo A (ed), Enfermedades infecciosas de Homo sapiens, 1st ed Fondo Editorial CIB, Medellin, Colombia.
-
- Deepe GS. 2015. Histoplasma capsulatum, p 2949–2962. In Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ (ed). Principles and practice of infectious diseases, 8th ed Elsevier, Philadelphia, PA.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

