Pro-resolving mediators promote resolution in a human skin model of UV-killed Escherichia coli-driven acute inflammation
- PMID: 29563331
- PMCID: PMC5926908
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.94463
Pro-resolving mediators promote resolution in a human skin model of UV-killed Escherichia coli-driven acute inflammation
Abstract
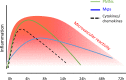
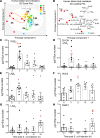
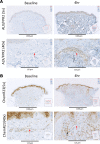
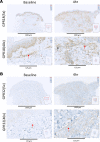
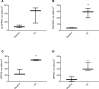
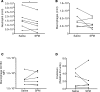
While the treatment of inflammatory disorders is generally based on inhibiting factors that drive onset of inflammation, these therapies can compromise healing (NSAIDs) or dampen immunity against infections (biologics). In search of new antiinflammatories, efforts have focused on harnessing endogenous pathways that drive resolution of inflammation for therapeutic gain. Identification of specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPMs) (lipoxins, resolvins, protectins, maresins) as effector molecules of resolution has shown promise in this regard. However, their action on inflammatory resolution in humans is unknown. Here, we demonstrate using a model of UV-killed Escherichia coli-triggered skin inflammation that SPMs are biosynthesized at the local site at the start of resolution, coinciding with the expression of receptors that transduce their actions. These include receptors for lipoxin A4 (ALX/FPR2), resolvin E1 (ChemR23), resolvin D2 (GPR18), and resolvin D1 (GPR32) that were differentially expressed on the endothelium and infiltrating leukocytes. Administering SPMs into the inflamed site 4 hours after bacterial injection caused a reduction in PMN numbers over the ensuing 6 hours, the phase of active resolution in this model. These results indicate that in humans, the appearance of SPMs and their receptors is associated with the beginning of inflammatory resolution and that their therapeutic supplementation enhanced the resolution response.
Keywords: Eicosanoids; Inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Segal AW, Peters TJ. Characterisation of the enzyme defect in chronic granulomatous disease. Lancet. 1976;1(7974):1363–1365. - PubMed
-
- Morgenstern DE, Gifford MA, Li LL, Doerschuk CM, Dinauer MC. Absence of respiratory burst in X-linked chronic granulomatous disease mice leads to abnormalities in both host defense and inflammatory response to Aspergillus fumigatus. J Exp Med. 1997;185(2):207–218. doi: 10.1084/jem.185.2.207. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Franceschi C, Campisi J. Chronic inflammation (inflammaging) and its potential contribution to age-associated diseases. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2014;69 Suppl 1:S4–S9. - PubMed
-
- Vane JR, Botting RM. Anti-inflammatory drugs and their mechanism of action. Inflamm Res. 1998;47 Suppl 2:S78–S87. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

