Endothelial cell Pannexin1 modulates severity of ischemic stroke by regulating cerebral inflammation and myogenic tone
- PMID: 29563335
- PMCID: PMC5926909
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.96272
Endothelial cell Pannexin1 modulates severity of ischemic stroke by regulating cerebral inflammation and myogenic tone
Abstract
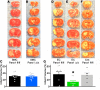
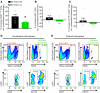
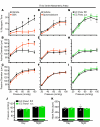
Ischemic stroke is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality in the US; however, there currently exists only one effective acute pharmacological therapeutic intervention. Purinergic signaling has been shown to regulate vascular function and pathological processes, including inflammation and arterial myogenic reactivity, and plays a role in ischemic stroke outcome. Purinergic signaling requires extracellular purines; however, the mechanism of purine release from cells is unclear. Pannexin1 (Panx1) channels are potentially novel purine release channels expressed throughout the vascular tree that couples regulated purine release with purinergic signaling. Therefore, we examined the role of smooth muscle and endothelial cell Panx1, using conditional cell type-specific transgenic mice, in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury outcomes. Deletion of endothelial cell Panx1, but not smooth muscle cell Panx1, significantly reduced cerebral infarct volume after ischemia/reperfusion. Infiltration of leukocytes into brain tissue and development of cerebral myogenic tone were both significantly reduced when mice lacked endothelial Panx1. Panx1 regulation of myogenic tone was unique to the cerebral circulation, as mesenteric myogenic reactivity and blood pressure were independent of endothelial Panx1. Overall, deletion of endothelial Panx1 mitigated cerebral ischemic injury by reducing inflammation and myogenic tone development, indicating that endothelial Panx1 is a possible novel target for therapeutic intervention of ischemic stroke.
Keywords: Mouse models; Neuroscience; Stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

