Quercetin attenuates neuronal cells damage in a middle cerebral artery occlusion animal model
- PMID: 29563391
- PMCID: PMC5938200
- DOI: 10.1292/jvms.17-0693
Quercetin attenuates neuronal cells damage in a middle cerebral artery occlusion animal model
Abstract
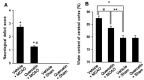
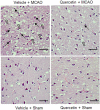
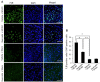
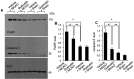
Cerebral ischemia is a neurological disorder with high mortality. Quercetin is a flavonoid compound that is abundant in vegetables and fruits. It exerts anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects. This study investigated the neuroprotective effects of quercetin in focal cerebral ischemia. Male Sprague-Dawley rats were subjected to middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) to induce focal cerebral ischemia. Quercetin or vehicle was injected 30 min before the onset of ischemia. A neurological function test, brain edema measurement, and 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride staining were performed to elucidate the neuroprotective effects of quercetin. Western blot analysis was performed to observe caspase-3 and poly ADP-ribose polymerase (PARP) protein expression. MCAO leads to severe neuronal deficits and increases brain edema and infarct volume. However, quercetin administration attenuated the MCAO-induced neuronal deficits and neuronal degeneration. We observed increases in caspase-3 and PARP protein levels in MCAO-operated animals injected with vehicle, whereas quercetin administration attenuated these increases in MCAO injury. This study reveals the neuroprotective effect of quercetin in an MCAO-induced animal model and demonstrates the regulation of caspase-3 and PARP expression by quercetin treatment. These results suggest that quercetin exerts a neuroprotective effect through preventing the MCAO-induced activation of apoptotic pathways affecting caspase-3 and PARP expression.
Keywords: PARP; caspase-3; neuroprotection; quercetin.
Figures

References
-
- Ahmad A., Khan M. M., Hoda M. N., Raza S. S., Khan M. B., Javed H., Ishrat T., Ashafaq M., Ahmad M. E., Safhi M. M., Islam F.2011. Quercetin protects against oxidative stress associated damages in a rat model of transient focal cerebral ischemia and reperfusion. Neurochem. Res. 36: 1360–1371. doi: 10.1007/s11064-011-0458-6 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

