Attitudes towards Prosthodontic Clinical Decision-Making for Edentulous Patients among South West Deanery Dental Foundation Year One Dentists
- PMID: 29563454
- PMCID: PMC5851257
- DOI: 10.3390/dj4020012
Attitudes towards Prosthodontic Clinical Decision-Making for Edentulous Patients among South West Deanery Dental Foundation Year One Dentists
Abstract
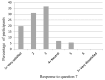
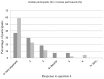
The aim of this study was to describe Dental Foundation year one dentists' attitudes towards prosthodontic decision making for edentulous patients, and identify whether there are gender differences in these attitudes. All South West Deanery trainees were invited to take part in the study between May and June 2011 and a previously piloted questionnaire was administered to the trainees by their training programme directors. The questionnaire posed questions based upon a clinical scenario of discussing treatment options with patients. Seventy-two questionnaires were used in the analysis (91% overall response rate). Trainees perceived their own values to be less important than the patient's values (p < 0.001) in decision making, but similar to the patient's friend's/relative's values (p = 0.1). In addition, the trainees perceived the patient's values to be less important than their friend's/relatives (p < 0.001). Sixty-six per cent of trainees acknowledged an influence from their own personal values on their presentation of material to patients who are in the process of choosing among different treatment options, and 87% thought their edentulous patients were satisfied with the decision making process when choosing among different treatment options. Fifty-eight per cent of trainees supported a strategy of negotiation between patients and clinicians (shared decision making). There was no strong evidence to suggest gender had an influence on the attitudes towards decision making. The finding of a consensus towards shared decision making in the attitudes of trainees, and no gender differences is encouraging and is supportive of UK dental schools' ability to foster ethical and professional values among dentists.
Keywords: decision making; dentist; dentures; prosthetics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- General Dental Council (GDC) Standards for the Dental Team. General Dental Council; London, UK: 2013. [(accessed on 10 May 2015)]. Available online: http://www.gdc-uk.org/Dentalprofessionals/Standards/Documents/Standards%....
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

